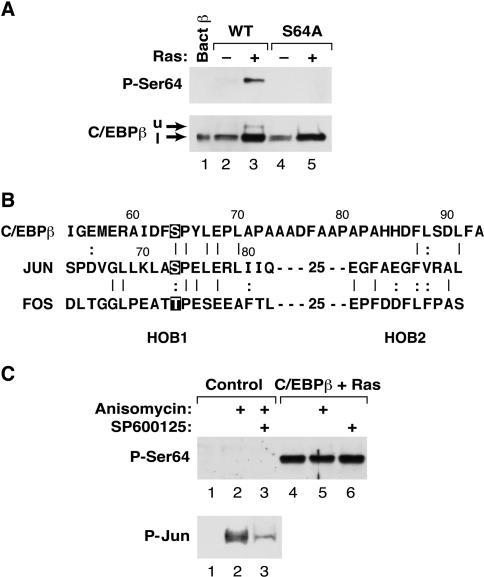
FIG. 3.
Analysis of Ser64 phosphorylation using a phosphospecific antibody. (A) Characterization of an anti-P-Ser64 C/EBPβ antiserum. Lysates were prepared from L cells expressing wild-type or S64A C/EBPβ, with or without RasV12, and analyzed by Western blotting using either anti-P-Ser64 C/EBPβ (upper panel) or a conventional C/EBPβ antiserum (lower panel). The upper band (u) recognized by the anti-P-Ser64 antibody and the lower band (l) recognized predominantly by the conventional antibody are indicated by arrows. (B) Sequence alignment of the TAD regions from C/EBPβ, c-Jun, and c-Fos. Ser64 in C/EBPβ, the JNK site in c-Jun (Ser73), and the analogous Thr phosphoacceptor in c-Fos are highlighted. HOB1 and HOB2, homology boxes 1 and 2. (C) Ser64 is not a target of JNKs. L cells were mock transfected (control) or transfected with C/EBPβ and RasV12; then they were either left untreated or treated for 30 min with anisomycin (to activate JNKs) and/or the JNK inhibitor SP600125. Lysates were prepared and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-P-Ser64 (upper panel) or anti P-Jun (lower panel) antibodies.