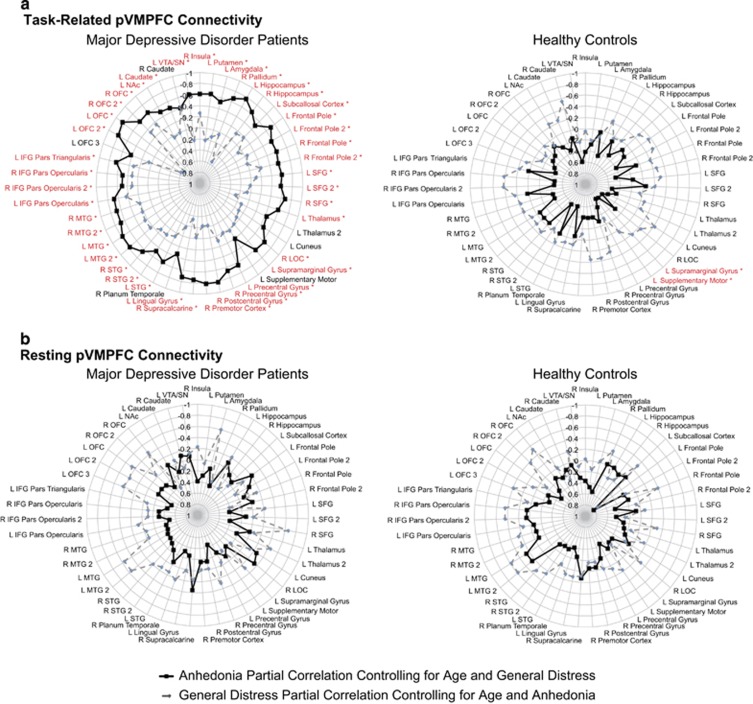
Figure 3.
Dissociable effects of anhedonia and general distress on posterior ventromedial prefrontal cortex (pVMPFC) connectivity in major depressive disorder (MDD) patients. (a) pVMPFC connectivity during the pleasant music listening task dissociates anhedonia from general distress in patients with MDD. Solid lines depict strength of partial correlations between pVMPFC connectivity and anhedonia after controlling for age and general distress. Dashed lines depict the strength of partial correlations between pVMPFC connectivity and general distress after controlling for age and anhedonia. Links that were significant for anhedonia after controlling for general distress and age after correction for multiple comparisons are shown in red (*P<0.05, FDR corrected). (b) The pVMPFC connectivity during resting state did not dissociate anhedonia from general distress in either group.