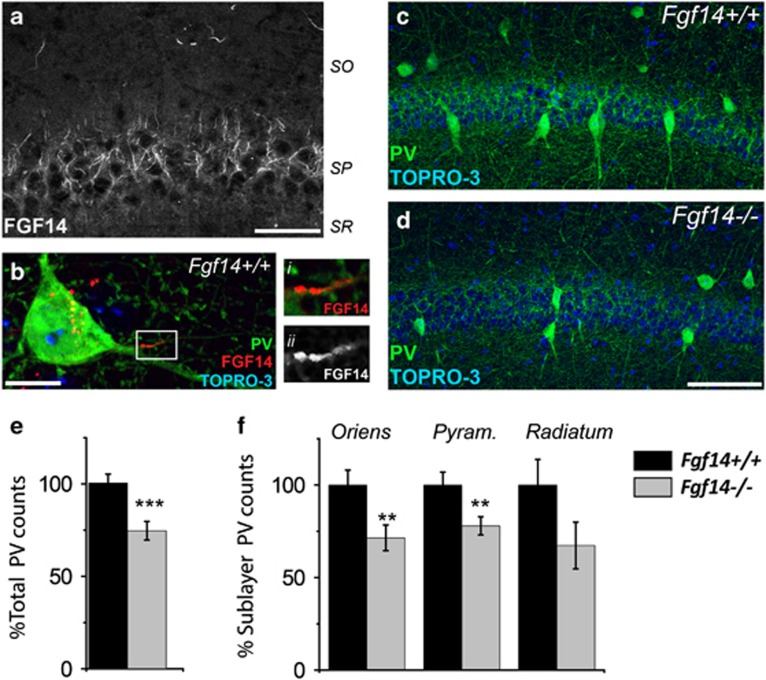
Figure 1.
Genetic deletion of Fgf14 results in structural changes in the CA1 parvalbumin (PV) interneurons. (a) FGF14 immunoreactivity is detectable at the axonal initial segment (AIS) of cells in CA1. (b) FGF14 (red) expressed in the soma and AIS of PV interneurons (green), i and ii represent zooms of the boxed area. (c, d) PV interneurons in the CA1 region of Fgf14+/+ and Fgf14−/− mice and respective higher resolution views of PV somas (i and ii). (e, f) Quantification of total PV interneurons in CA1 (380 cells in Fgf14+/+ and 282 in Fgf14−/−), and in specific subfields (oriens, pyramidalis and radiatum). Data represent mean±s.e.m., ***P<0.001; **P<0.02; *P<0.05 statistical differences were assessed by Student's t-test or non-parametric Mann–Whitney test. Scale bars, 40 μm (a); 10 μm (b); 100 μm (d).