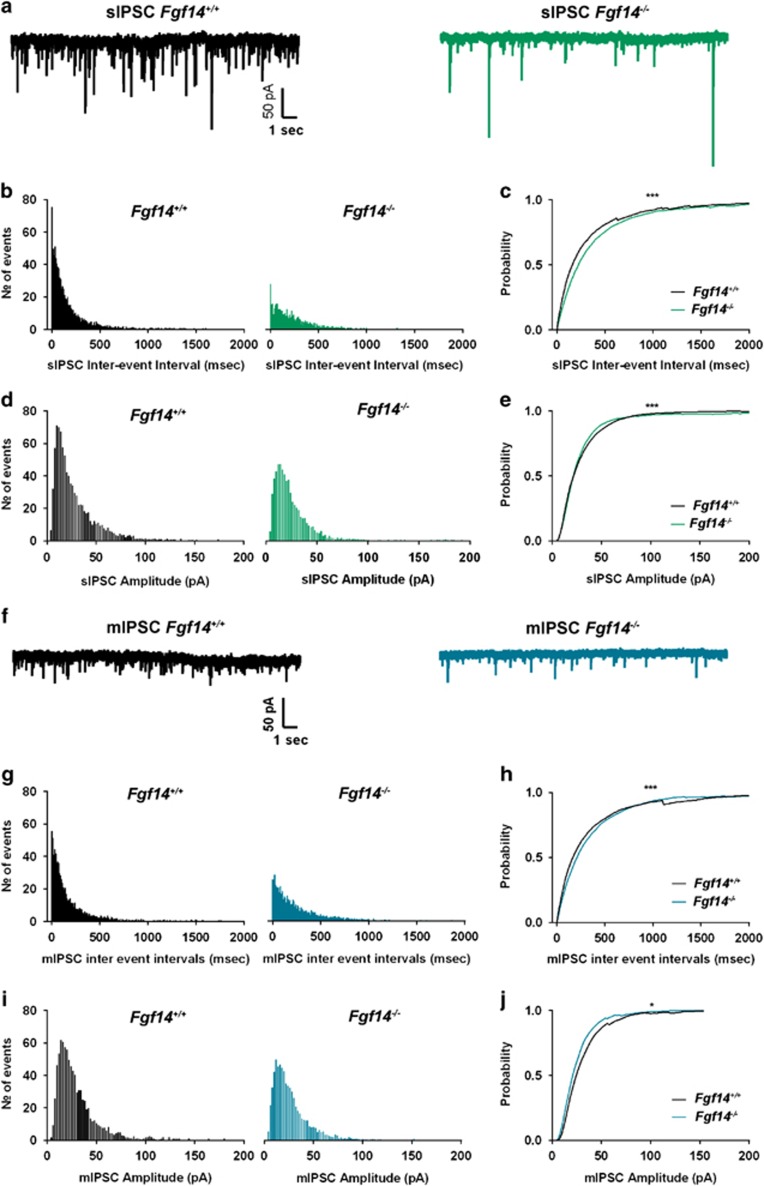
Figure 3.
Genetic deletion of Fgf14 impairs GABAergic transmission in the CA1 region. Representative traces of whole-cell patch-clamp recordings showing effect of Fgf14 ablation on spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic current (sIPSCs) (a) and miniature inhibitory postsynaptic current (mIPSCs) (f). (b) Inter-event-interval distribution of spontaneous GABAergic events in Fgf14+/+ (n=8 cells) and Fgf14−/−(n=10 cells) mice. (c) Inter-event-interval cumulative distribution plot for Fgf14+/+ and Fgf14−/−(sIPSCs; ***P<0.001, Kolmogorov–Smirnov test). (d) Amplitude distribution of spontaneous GABAergic events in Fgf14+/+ (n=8 cells) and Fgf14−/− (n=10 cells) mice. (e) Amplitude cumulative distribution plot for Fgf14+/+ and Fgf14−/− sIPSCs (***P<0.001; Kolmogorov–Smirnov test). (g) Inter-event-interval distribution of miniature GABAergic events in Fgf14+/+ (n=6 cells) and Fgf14−/− (n=7 cells) mice. (h) Inter-event-interval cumulative distribution plot for Fgf14+/+ and Fgf14−/− mIPSCs (***P<0.001 with Kolmogorov–Smirnov test). (i) Amplitude distribution of miniature GABAergic events in Fgf14+/+ (n=6 cells) and Fgf14−/− (n=7 cells) mice. (j) Amplitude cumulative distribution plot for Fgf14+/+ and Fgf14−/− sIPSCs (*P<0.05; Kolmogorov–Smirnov test).