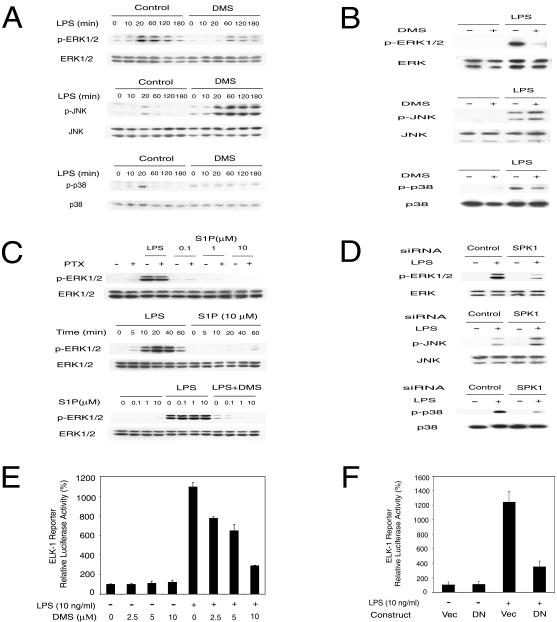
FIG. 4.
SPK mediates LPS-induced MAPK and Elk-1 activation. (A) MAPK activation by LPS was modulated by SPK inhibitor DMS in RAW 264.7 cells. The top panel shows that ERK1/2 activation by LPS was inhibited by DMS. The middle panel shows that JNK activation by LPS was enhanced by DMS. The bottom panel shows that p38 activation by LPS was inhibited by DMS. RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with or without 10 μM DMS for 30 min and then stimulated with 10 ng of LPS/ml in the indicated time course. The phospho-MAPK and total MAPK in cell lysates were detected by Western blot. (B) MAPK activation by LPS was modulated by SPK inhibitor DMS in primary HMs. The top panel shows that ERK1/2 activation by LPS was inhibited by DMS. The middle panel shows that JNK activation by LPS was enhanced by DMS. The bottom panel shows that p38 activation by LPS was inhibited by DMS. HMs were pretreated with or without 10 μM DMS for 30 min and then stimulated with 10 ng of LPS/ml for 20 min. MAPK activation was assayed as described for panel A. (C) LPS activation of ERK1/2 is not through membrane S1P receptor. The upper panel shows that PTX did not block LPS-induced ERK1/2 activation. RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with or without 100 ng of PTX/ml for 3 h and then stimulated with 10 ng of LPS/ml for 20 min or indicated concentrations of S1P for 10 min. The middle panel shows that extracellular S1P does not activate ERK1/2 in RAW 264.7 cells. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with 10 ng of LPS/ml or 10 μM S1P for the indicated time. The lower panel shows that extracellular S1P does not rescue the inhibition of LPS-induced ERK1/2 activation by DMS. RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with or without 10 μM DMS for 30 min and then stimulated with 10 ng of LPS/ml and indicated concentrations of S1P for 20 min. ERK1/2 activation was assayed as described for panel A. (D) MAPK activation by LPS was modulated by SPK1 siRNA. The top panel shows that SPK1 siRNA blocked ERK1/2 activation by LPS. The middle panel shows that SPK1 siRNA enhanced JNK activation by LPS. The bottom panel shows that SPK1 siRNA blocked p38 activation by LPS. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with 175 nM siRNA for 24 h and then stimulated with LPS (10 ng/ml) for 20 min. MAPK activation was assayed as described for panel A. (E) Elk-1 activation by LPS was inhibited by the SPK inhibitor DMS. RAW 264.7 cells were transfected with the Elk-1 trans-reporting system (Stratagene) along with a pEF-β-Gal vector. Two days after transfection, cells were stimulated with LPS (10 ng/ml) in the presence of the indicated concentrations of DMS for 12 h. Reporter luciferase activity was measured using the luciferase assay system (Promega). Data were normalized with β-Gal activity in each sample. (F) DN-SPK1 inhibited LPS-induced Elk-1 activation. RAW 264.7 cells were transfected with the Elk-1 trans-reporting system, pEF-β-Gal and either a control vector or DN-SPK1. The reporter assay was conducted as described for panel E.