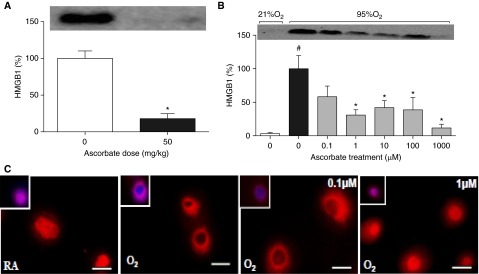
Figure 5.
AA decreases the hyperoxia-induced release of high-mobility group box protein B1 (HMGB1) by inhibiting its translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Male C57BL/6 mice, exposed to 98% O2 or higher for 48 hours, were inoculated with PA (1 × 107 CFU) intratracheally. Mice were randomized to receive either AA (50 mg/kg) or saline intraperitoneally. HMGB1 levels in the BALF were analyzed by Western blot analysis. *P ≤ 0.05 compared with hyperoxia control group (A). RAW 264.7 cells either remained at RA (21% O2) or were exposed to 95% O2 for 24 hours with AA (0–1,000 μM). HMGB1 levels in cell culture media were analyzed by Western blot analysis. The data obtained are represented in percentage of the 95% O2 control group. *P ≤ 0.05 compared with 95% O2 (0 μM) control group; #P ≤ 0.05 compared with 21% O2 (0 μM) control group (B). The translocation of HMGB1 was assessed by immunostaining the cells with anti-HMGB1 antibody (red). DAPI stain was used to visualize the nuclei (blue). Scale bars: 10 μm (C). Each value represents the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments.