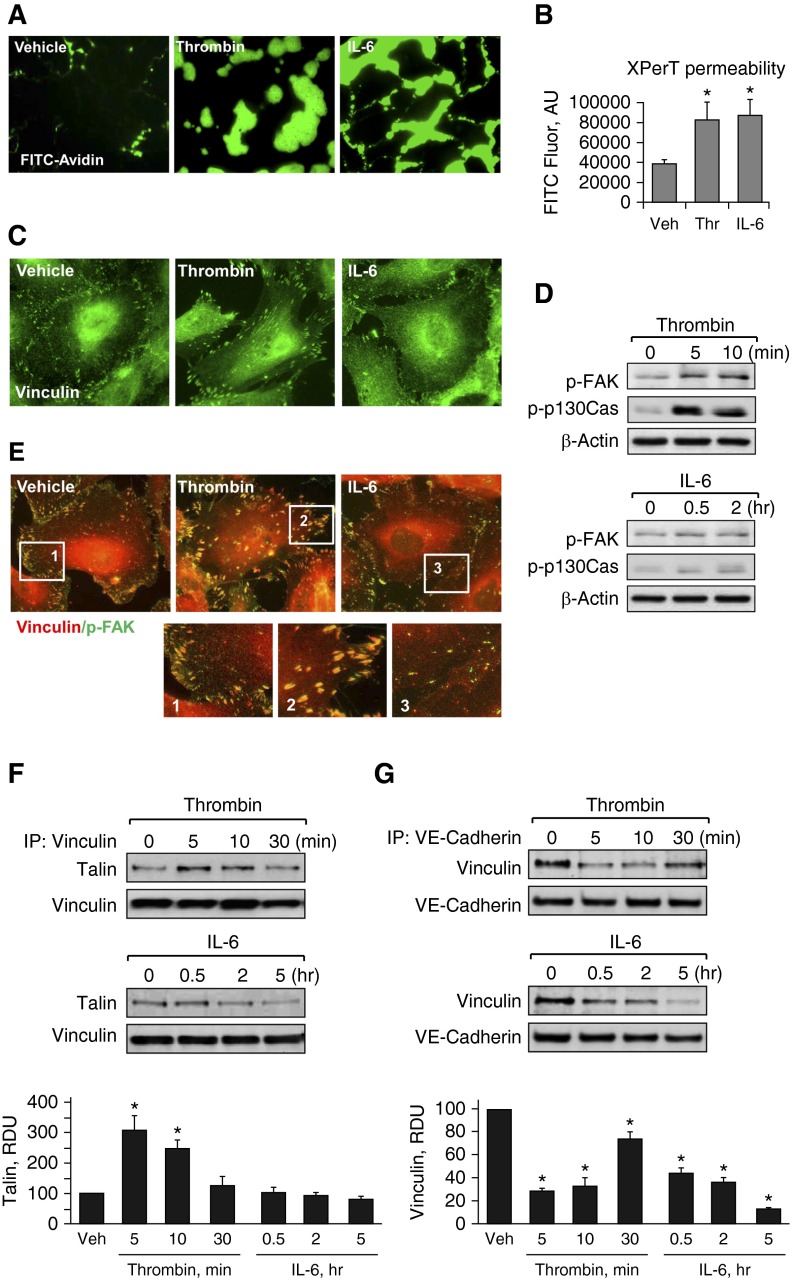
Figure 1.
Effects of thrombin and IL-6 on endothelial permeability and focal adhesion (FA) remodeling. (A and B) Human pulmonary artery endothelial cells (HPAECs) grown on glass coverslips (A) or in 96-well plates (B) with immobilized, biotinylated gelatin (0.25 mg/ml) were treated with thrombin (0.2 U/ml, 10 min) or IL-6 and soluble receptor (SR; 30 ng/ml and 60 ng/ml, 5 h), followed by addition of fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-avidin (25 µg/ml, 3 min). Unbound FITC-avidin was removed, and FITC fluorescence (Fluor) was measured; n = 4; *P < 0.05 versus vehicle. (C) Cells grown on coverslips were stimulated with thrombin (0.2 U/ml, 10 min) or IL-6 and SR (30 ng/ml and 60 ng/ml, 5 h). FA remodeling was analyzed by immunofluorescence staining for vinculin. (D) Levels of phosphorylated FA kinase (p-FAK) and Crk-associated substrate (p130Cas) were determined by Western blot analysis using specific antibodies. Equal protein loading was confirmed by determination of β-actin content in total cell lysates. (E) HPAECs were stimulated with thrombin or IL-6/SR (10 min and 5 h, respectively) followed by double immunofluorescence staining with antibodies against vinculin (red) and p-FAK (green). Merged images depict areas of vinculin and p-FAK colocalization, which appear in yellow. Higher-magnification insets show details of FA localization. (F and G) Co-immunoprecipitation assays using antibodies to vinculin (F) or vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin (G) were performed, and talin or vinculin content in the immunoprecipitates was detected using the appropriate antibody. Bar graphs depict quantitative analysis of Western blot data; n = 3; *P < 0.05 versus vehicle. AU, arbitrary units; IP, immunoprecipitation; RDU, relative density unit; Thr, thrombin; Veh, vehicle.