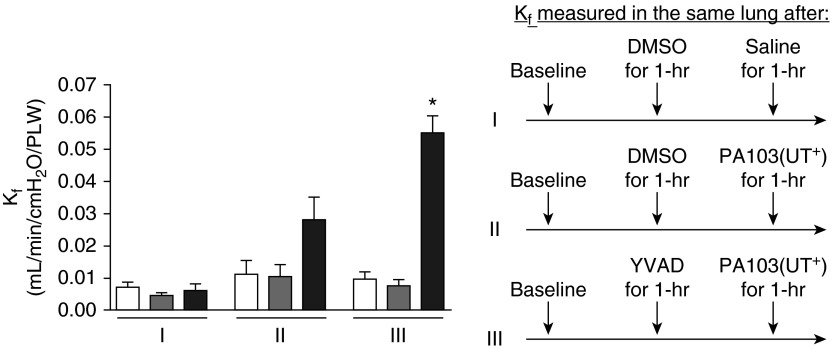
Figure 4.
Caspase-1 inhibition in P. aeruginosa–infected rat lung increases permeability. Endothelial barrier function in isolated rat lungs was measured as hydraulic permeability (filtration coefficient [Kf]). The schematic on the right depicts the serial treatment protocol for lungs assayed in each segment. Segment I: serial Kf measurements taken at baseline (white bar), 1 hour after addition of DMSO (inhibitor vehicle control) to the perfusate at a final concentration of 0.3% (gray bar), and 1 hour after addition of 200 µl saline (infection vehicle control) to the perfusate (black bar). Segment II: serial Kf measurements taken at baseline (white bar), 1 hour after addition of DMSO to the perfusate (gray bar), and 1 hour after addition of 107 CFU of PA103(UT+) suspended in 200 µl saline to the perfusate (black bar, infected control). Segment III: serial Kf measurements taken at baseline (white bar), 1 hour after addition of a caspase-1 inhibitor (YVAD) to the perfusate at a final concentration of 30 µM (gray bar), and 1 hour after PA103(UT+) infection (black bar, experimental). For each segment, n = 3 rat lungs. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA (Newman-Keuls post hoc test) when comparing within segment III.