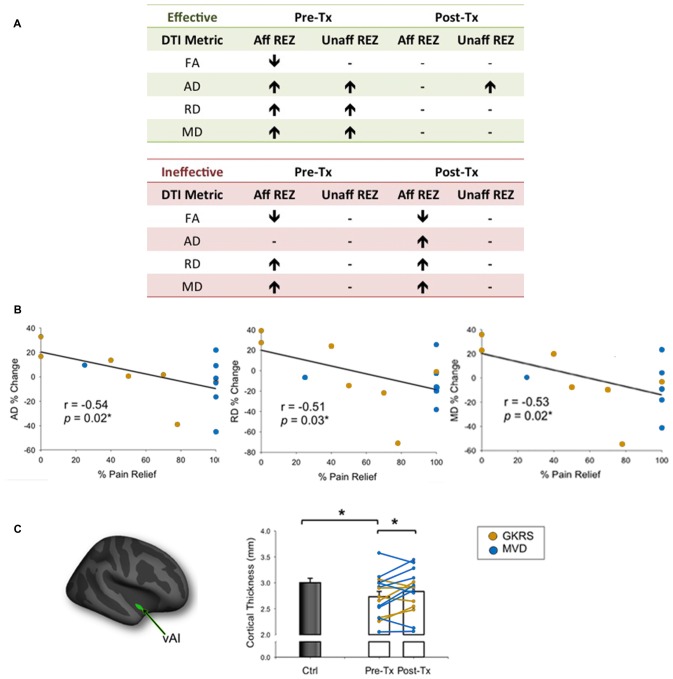
Figure 7.
Effects of neurosurgical treatment for TN on trigeminal REZ and brain abnormalities (A). Patients undergoing neurosurgical treatment for TN were deemed to have either effective or ineffective treatment based on a threshold of ≥75% reduction in baseline pain intensity ratings. Only patients that had effective treatment showed a reversal of pre-treatment trigeminal REZ abnormalities in FA, AD, RD and MD following treatment (green box). In contrast, pre-treatment REZ abnormalities persisted in patients that had ineffective treatment (green box). Arrows indicate direction of abnormalities relative to controls. (B) The degree of normalization of AD, RD and MD abnormalities only at the affected trigeminal REZ was associated with the degree of pain relief achieved by TN patients. (C) The vAI (green cluster on inflated brain) was the only gray matter region to normalize in patients following effective treatment only. Specifically, prior to treatment patients had significantly thinner vAI thickness compared to controls. Following treatment, vAI thickness significantly increased to become comparable to control vAI thickness. Bar graphs of mean CT values ± SEM (in mm) are shown for controls (black bars) and patients (white bars). Individual patient data are also shown pre- and post-treatment, with patients who received GKRS in orange, and MVD surgery in blue. Tx, treatment; Aff REZ, affected root entry zone; Unaff REZ, unaffected root entry zone; FA, fractional anisotropy; RD, radial diffusivity; MD, mean diffusivity; AD, axial diffusivity; Ctl, controls; vAI, ventral anterior insula; GKRS, Gamma Knife Radiosurgery; MVD, microvascular decompression. Panels (B,C) have been adapted from DeSouza et al. (2015) with permission (Rightslink license number: 3823931191470). Asterisks indicate significance at p < 0.05 level.