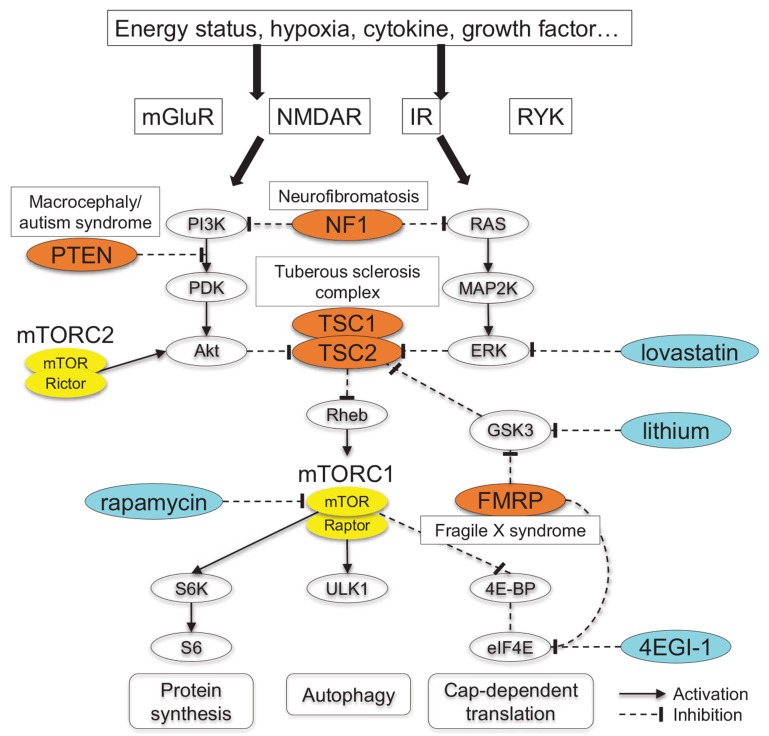
Fig. (1).
Signaling pathway involving mTORC1. Various stimuli converge on mTORC1 pathway via a number of routes. mTORC1 activation impacts on different cellular physiology, such as protein synthesis, cap-dependent mRNA translation, and autophagy. Here mutations in TSC1/2, PTEN, FMR1, and NF1 cause constitutive mTORC1 activation and syndromic ASD. Akt, protein kinase B; eIF4E, eukaryotic initiation factor 4E; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; 4E-BP, 4E-binding protein; FMRP, fragile X mental retardation protein; GSK3, glycogen synthase kinase 3; IR, insulin receptor; MAP2K, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; mGluR, metabotropic glutamate receptor; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NF1, neurofibromin; NMDAR, NMDA receptor; PDK, phosphoinositide-dependent kinase; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; RAS, rat sarcoma; Rheb, Ras homolog enriched in brain; RYK, receptor-like tyrosine kinase; S6K, p70 ribosomal S6 kinase; TSC, tuberous sclerosis complex; ULK1, unc51-like kinase 1.