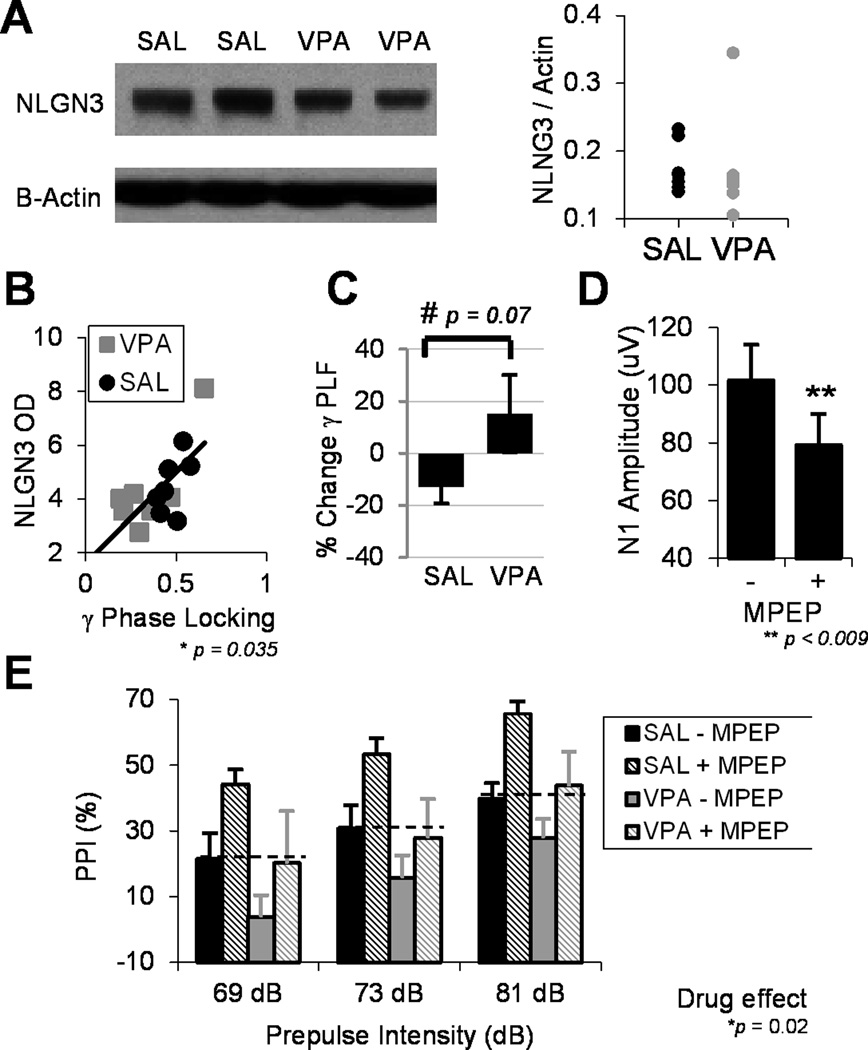
Fig 4.
Biomarkers are related to the expression of the autism risk gene neuroligin 3 and may be useful therapeutic targets. A) A western blot of neuroligin 3 and β-actin indicates no group differences between SAL and VPA treated adult mice (p=0.1). B) However, NLGN3 protein expression (optical density) significantly predicts gamma phase-locking (R2=0.46, p=0.035, corrected). Note, the VPA-group outlier fits the linear correlation, as it also does in the regression of gamma PLF and PPI (Fig 3B). C) The effect of the mGluR5 antagonist MPEP was assessed on gamma PLF. The plot demonstrates the change in phase-locking (%) after drug administration. A trending interactive effect across SAL and VPA groups suggests that MPEP reduced PLF in the SAL group but boosted gamma synchrony in VPA exposed mice. D) Across both groups, MPEP reduced cortical excitability as measured by N1 amplitude. E) MPEP increased PPI across VPA and SAL groups. Dashed lines indicate that MPEP normalizes PPI deficits in VPA exposed mice. All figures indicate mean ± s.e.m.