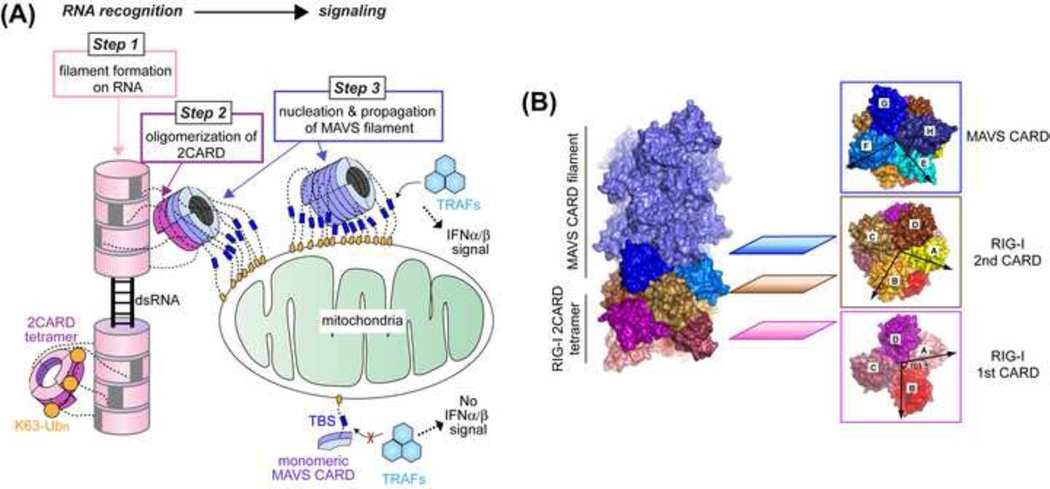
Fig. 2. Oligomerization of receptors and adaptor during RIG-I & MDA5 signal activation.
(A) Three steps of oligomerization involved during RNA recognition and signaling by RIG-I and MDA5. First, the RNA-binding domains (helicase-CTD) of RIG-I and MDA5 oligomerize on dsRNA (as shown in Fig. 1). Second, the signaling domain (2CARD) of RIGI/ MDA5 oligomerizes through proximity-induced and/or K63-Ubn-mediated mechanisms. Finally, the oligomerized 2CARD nucleates the MAVS filament through the interaction between RIG-I2CARD and MAVSCARD. The filamentous MAVS then activates the downstream signaling pathway by recruiting TRAF molecules to TRAF-binding sites (TBSs) that are clustered on the surface of mitochondria. The image was modified from Ref. 47.
(B) A composite structure obtained by overlaying the structures of the helical tetramer of the RIG-I2CARD:MAVSCARD complex and the MAVSCARD filament. These structures were reported in Ref. 47 and the image was modified from this paper.