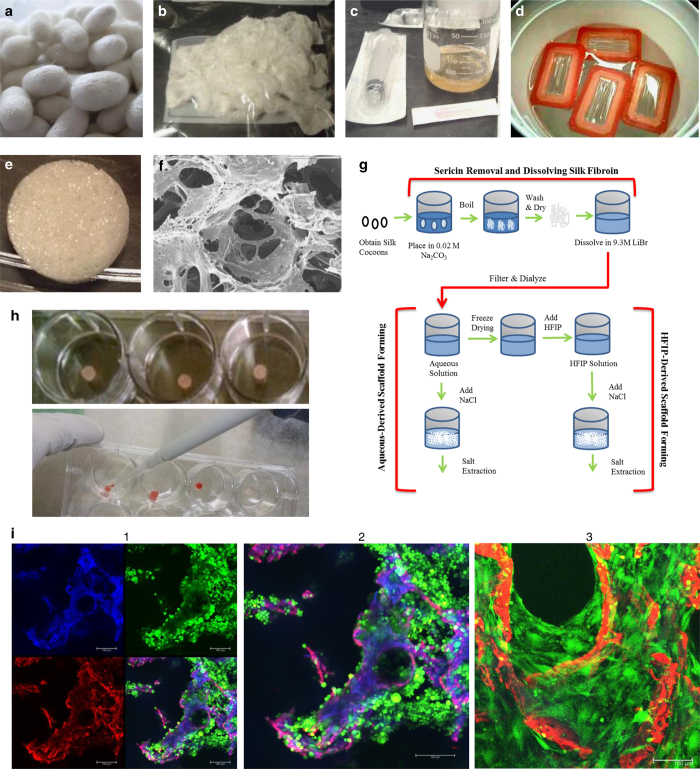
Figure 1.
Generation, seeding and analysis of silk scaffolds for tissue-engineered bone-cancer models. (a) Silk worms (Bombyx mori) are grown on mulberry leaves and produce cocoons as they begin to undergo metamorphosis into silk moths. (b) Cleaned cocoons are boiled to separate silk sericin from silk fibroin and air dried to produce fibroin with a cottony texture. (c) Dried silk fibroin is then dissolved in LiBr to produce a highly concentrated silk solution. (d) This solution is then dialyzed with dialysis cassettes to remove LiBr ions and purify the silk solution. Silk solution can then be freeze-dried and re-dissolved by HFIP, or used directly to make silk scaffolds. (e) Silk solution is poured into molds and NaCl crystals are added slowly over the silk solution to crosslink silk protein to create a porous scaffold. After 3 days, salt is washed from the scaffolds and scaffolds are cut to size. (f) Silk scaffolds can be imaged with a scanning electron microscope (SEM) for high-resolution imaging. (g) Schematic of silk scaffolds making procedures. (h) Scaffolds are soaked in well plates (top) with culture media to prepare for seeding, and then cells are seeded with a pipette (bottom). (i) Whole flushed BM cells from C3H mice were seeded onto silk scaffolds and imaged with live/dead confocal imaging 3 days after seeding. (1) Silk autofluorescence is seen in the blue channel, dead cells (ethidium homodimer-1) and autofluorescence of silk is seen in the red channel, and live cells (calcein) are seen in the green channel. (2) Magnification of the overlay from shows scaffold in purple/pink, live cells in green, and a few dead cells, indicated in red. (3) Live-dead (calcein-green/ethidium homodimer-1/red) staining confocal imaging of mouse MSCs (green) first expanded in vitro on tissue culture plastic (2D), and then seeded at passage 2 on silk scaffolds (red) and cultured for 9 days in mMSC expansion media. Cells can be seen growing off the scaffolds and into the pores throughout the scaffolds.