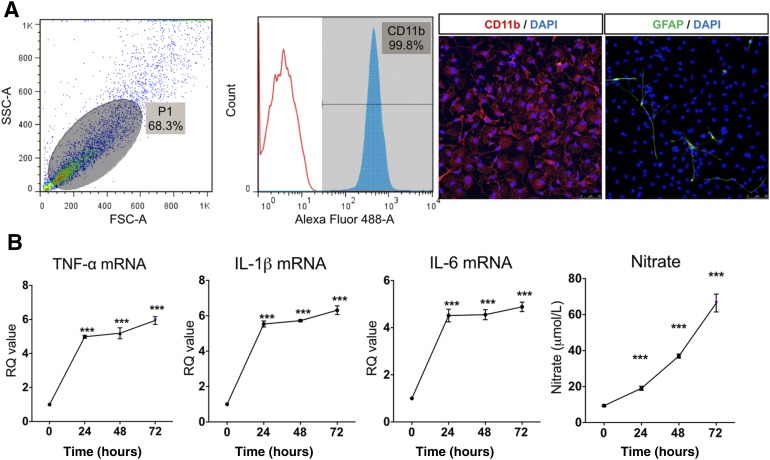
Figure 1.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory reaction in primary cultured microglia. (A): Characteristics of primary cultured microglia by flow cytometry and immunocytochemistry. The primary cultured cells were 99.8% CD11b positive, confirming pure microglia isolation. Glial fibrillary acidic protein, an astrocyte marker, was observed in less than 1% of the cells. (B): LPS, 100 ng/ml, was applied to primary cultured microglia for 24, 48, and 72 hours. LPS increased mRNA expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and inducible nitric oxide at all time points. Nitrate concentration gradually increased with LPS treatment duration. The data are means ± SEM of three independent experiments. ∗∗∗, p < .001 in comparison with control and 0 hour. Abbreviations: DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; FSC-A, forward scatter; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; hr, hour; IL, interleukin; RQ, relative quantity; SSC-A, side scatter; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.