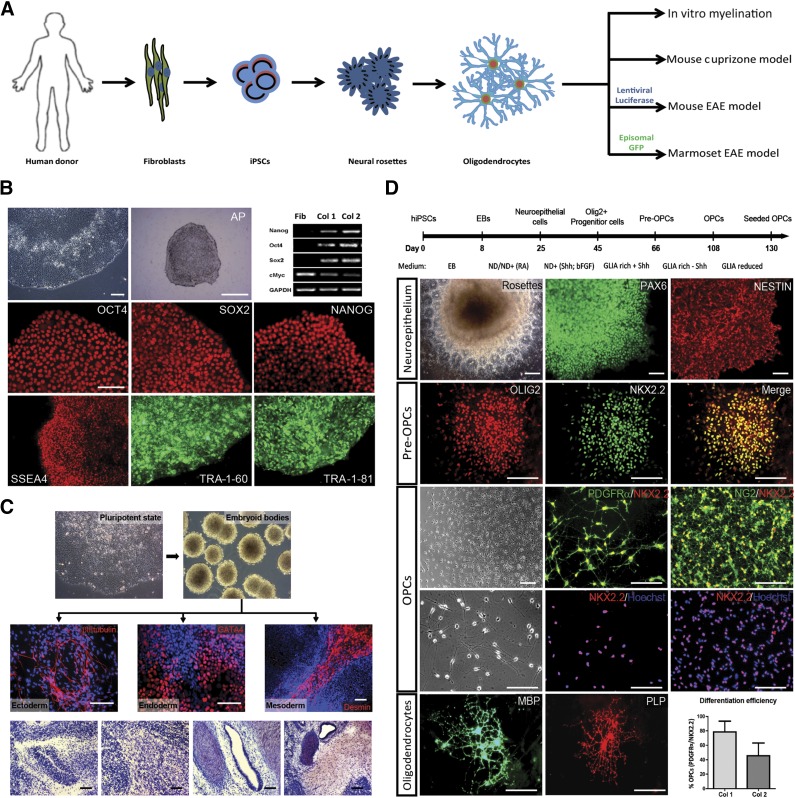
Figure 1.
Generation of human iPSCs and their differentiation toward OPCs. (A): Schematic representation of the study setup. (B): Generation and characterization of hiPSC clones: phase-contrast image of hiPSC-colony, AP staining of hiPSC-colony, and RT-PCR analysis illustrating the endogenous expression of pluripotence-associated genes in reprogrammed cells; immunocytochemical detection of pluripotence-associated transcription factors (OCT4, SOX2, NANOG) and membrane markers (SSEA4, TRA-1-60, TRA-1-81). Scale bars: 50 µm; 500 µm for AP section. (C): In vitro and in vivo spontaneous differentiation of hiPSCs. In vitro, hiPSCs differentiated via EBs into ectoderm (βIII-tubulin), endoderm (GATA4), and mesoderm (Desmin). In vivo differentiation of hiPSCs toward teratomas: hematoxylin and eosin staining of teratoma sections reveals the presence of neural, muscle, gland, and cartilage tissue. Scale bars: 50 µm; 200 µm for EB section. (D): Differentiation of hiPSCs into oligodendrocytes. Simplified scheme of differentiation protocol. Neuroepithelium: neural rosettes containing NSCs expressing PAX6 and NESTIN; pre-OPCs: immunostained for OLIG2 and NKX2.2; OPCs: phase-contrast image of OPCs migrating out of an oligosphere and (double) immunostainings for PDGFRα/NKX2.2, NKX2.2/Hoechst, NG2/NKX2.2, and NKX2.2/Hoechst; oligodendrocytes: mature oligodendrocytes immunostained for MBP and PLP. Scale bars: 50 µm. Efficiency of iPSC to OPC differentiation: expressed as percentage of PDGFRα/NKX2.2-positive cells of the total number of cells in one culture dish at the end of differentiation (n = 3, ± SD) in two different hiPSC lines. Abbreviations: AP, alkaline phosphatase; bFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor; EAE, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; EB, embryoid body; GFP, green fluorescent protein; hiPSC, human induced pluripotent stem cell; MBP, myelin basic protein; NSC, neural stem cell; OPC, oligodendrocyte precursor cell; PLP, myelin proteolipid protein; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; RT-PCR, reversetranscription-polymerase chain reaction.