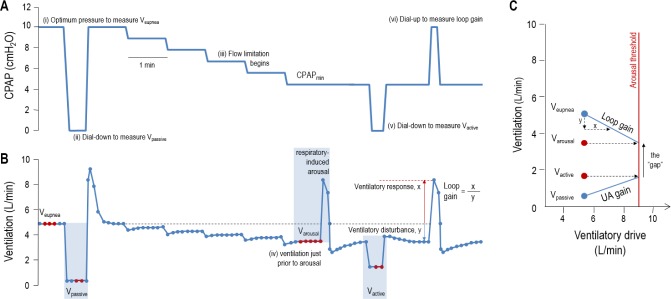
Figure 2.
Technique for determining the physiological traits using continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) dial-downs. The obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) traits are measured by manipulating CPAP during supine nonrapid eye movement (NREM) sleep (A) and measuring the changes in ventilation (B). After determining ventilation on optimum CPAP (Veupnea; i), the pressure was dialed down to measure passive V0 (ii), the ventilation at CPAP = 0 when pharyngeal muscles are inactive. CPAP was then lowered until flow limitation started (iii) and arousals occurred intermittently. Ventilation just prior to arousal (iv) was defined as the “ventilation causing arousal” (Varousal). During stable breathing between arousals, CPAP was dialed down or up to obtain active V0 (v) and loop gain (vi), respectively. Active V0 is the ventilation at CPAP = 0 when pharyngeal muscles are maximally activated. Loop gain is the ventilatory response (overshoot in ventilation above Veupnea) divided by the ventilatory disturbance (reduction in ventilation below Veupnea). (C) These four ventilations can be used to calculate the arousal threshold and upper airway response and illustrate how all four traits interact to manifest the absence or presence of OSA. After the patient's loop gain is known, the ventilation that causes arousal was translated into the ventilatory drive that causes the arousal, which is referred to as the arousal threshold (i.e., 9 L/min). When the arousal threshold is known, starting at the passive V0 we can say that if the ventilatory drive is increased to a level near the arousal threshold, then the pharyngeal muscles will activate and increase V0 to the measured level active V0. The slope of this line is called the upper airway gain (or response) and is a measure of the upper airway muscle function. The steeper this slope, the better the upper airway response to an increase in ventilatory drive, and the larger the distance between the active and passive V0. In order to avoid having OSA (i.e., achieve stable breathing), Vactive must be above Varousal.