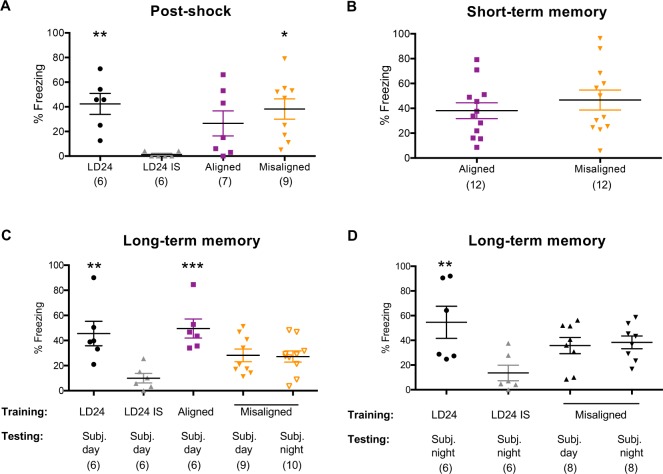
Figure 4.
Training during LD22 misaligned phases leads to impaired long-term memory consolidation of hippocampus-dependent contextual fear conditioning. (A) Post-shock freezing during training. Whereas immediate-shocked control animals (LD24 IS) do not freeze during training, LD24, LD22 aligned, and LD22 misaligned animals show normal freezing responses. One-way analysis of variance: F(3,24) = 4.51, P = 0.012; *P = 0.05, **P = 0.01 different from LD24 IS, Dunnett multiple comparisons test. (B) Freezing during short-term memory test. LD22 aligned and misaligned animals show similar short-term (15 min post-training) memory consolidation. Two-tailed Student t test: t(22) = 0.83, P = 0.41. (C) Training during the light phase of LD24 and LD22 aligned days, but not during the light phase of LD22 misaligned days, leads to higher test freezing responses than training with an immediate-shock. Bottom of x-axis indicates training and testing conditions; all animals were trained during the light phase; one-way analysis of variance: F(4,32) = 5.75, P = 0.0013. (D) Training during the dark phase of LD24 but not during the dark phase of LD22 misaligned days, leads to higher test freezing responses than training with an immediate shock. Bottom of x-axis indicates training and testing conditions; all animals were trained during the dark phase; one-way analysis of variance: F(3,24) = 4.05, P = 0.0184. *P = 0.05, **P = 0.01, ***P = 0.001 different from LD24 immediate shock, Dunnett multiple comparisons test. Number of animals is indicated in brackets.