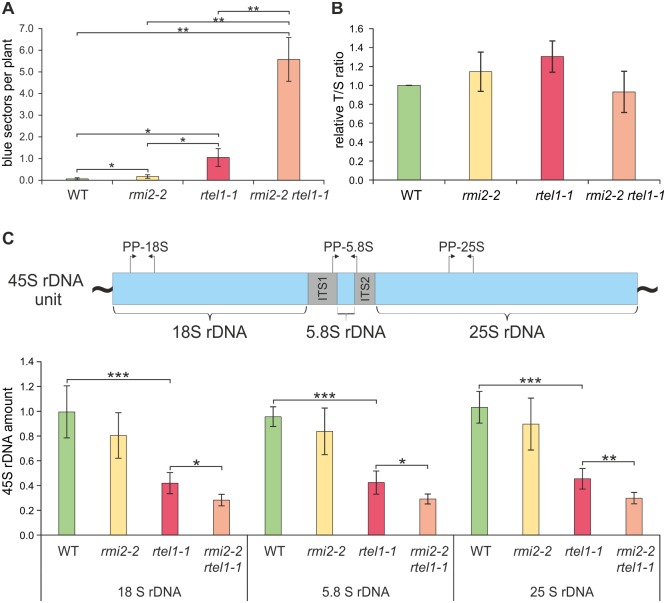
Fig 6. Loss of 45S rDNA repeats due to simultaneous defects in RMI2 and RTEL1.
(A) Genomic instability is associated with elevated recombination frequency, which was observed for rmi2-2 rtel1-1 mutants (n = 5). A tremendous 80-fold increase was shown for the double mutant rmi2-2 rtel1-1 compared to wild-type plants. (B) The length of telomeres was determined by the ratio of telomeric repeats to a single copy gene (T/S ratio). No statistically significant difference could be detected between wild-type and mutant plants (n = 3). (C) The double mutant rmi2-2 rtel1-1 exhibits a significant loss of 45S rDNA repeats compared to the single mutants and wild-type plants. Copy numbers of 18S, 5.8S and 25S rDNA sequences were analyzed independently with primer pairs as indicated in the schematic overview of one 45S rDNA unit (n = 6). Significant differences were calculated using the two-sample t-test, two-sided with no equal variance, p-values: *P ≤ 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. PP = primer pair, ITS = internal transcribed spacer.