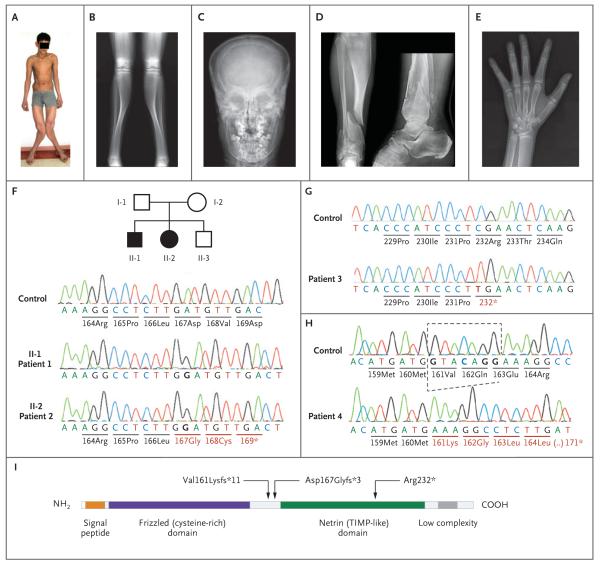
Figure 1. Clinical, Radiographic, and Molecular Findings.
Panel A shows Patient 1 at 16 years of age; he had deformation of the lower limbs with marked valgus of both legs. The expanded distal femora could be easily palpated above the knees. Panel B is a radiograph of the lower limbs in Patient 1, showing expanded metaphyses of the distal femora and proximal and distal tibiae with extremely thin cortexes. The appearance of the bone at the tibial midshaft, with thicker cortex, is relatively normal. Panel C is an anteroposterior skull radiograph of Patient 2, showing expansion of the diploe. Panel D is an anteroposterior and lateral projection of the distal right tibia in Patient 3, showing changes similar to those in Panel B. In addition, two fractures run through the abnormal metaphysis, and a third fracture runs through the distal fibula. Panel E is a hand radiograph of Patient 2 at 14 years of age, showing expanded metaphyses and thin cortexes at the distal radius, as well as expansion of the distal metacarpals and (to a lesser degree) of the phalanges. Panels F, G, and H show the nucleotide sequences of SFRP4 in controls, affected patients, and heterozygous family members. Patients 1 and 2 are homozygous for a nucleotide insertion in exon 2 (Panel F); as a result, amino acid residues 167 and 168 are replaced, and a stop codon is generated at position 169, leading to a truncated protein. Both parents and the brother are heterozygous for the insertion. Circles denote female family members, squares male family members, open symbols unaffected family members, and black symbols affected family members. Patient 3 is homozygous for a C-to-T transition that transforms codon 232 from arginine to a stop codon (Panel G). Patient 4 is homozygous for the deletion of 7 nucleotides; as a consequence, there is a stretch of 10 missense amino acids (codons 161–170), followed by a premature termination at codon 171 (Panel H). Panel I is a diagram of the sFRP4 protein, illustrating the two main domains as well as the positions of the three mutations found in the patients.