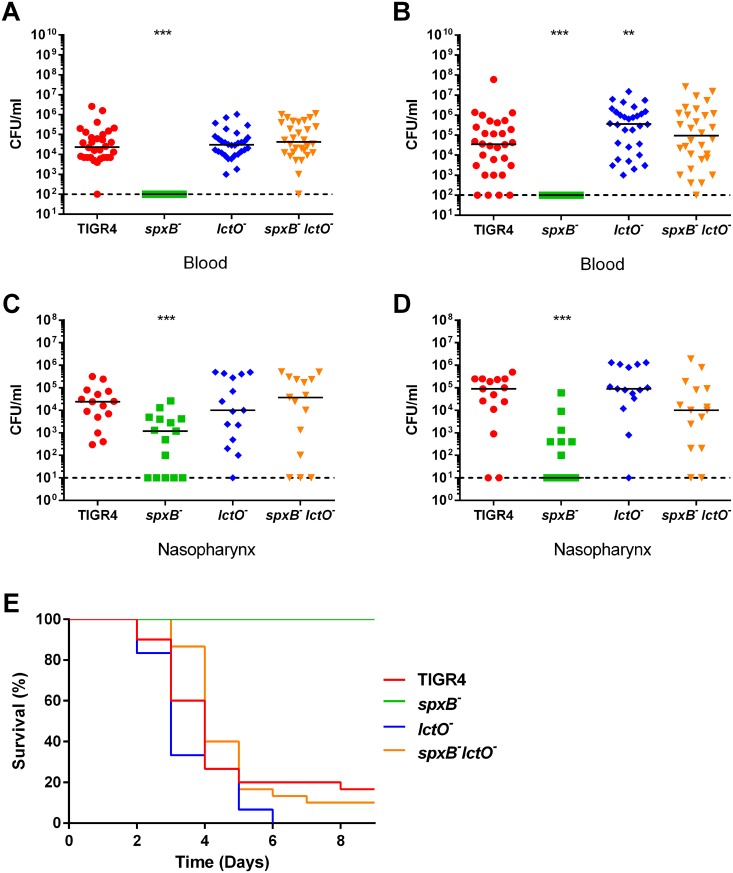
Fig 6. TIGR4 spxB mutant has reduced virulence in an IN mouse model.
BALB/c mice were infected IN with 1 x 107 cells. Bacterial presence in the blood in mice infected with TIGR4 strains was determined by detection of colony forming units (CFU/mL) at 24 hours (A) and 48 hours (B) post infection. In the same mice, bacterial carriage in the nasopharynx was determined at 24 hours (C) and 48 hours (D) post infection. Survival of mice was followed for 9 days (E). For each time-point of bacterial titers, mutant strains were compared to wild type using nonparametric Mann-Whitney t test; * p = 0.05–0.01, ** p = 0.01–0.001, *** p<0.001. Survival data were analyzed using the Mantel-Cox log rank test. p<0.0001 for TIGR4 spxB mutant compared to wild type; p = 0.0458 for TIGR4 lctO mutant compared to wild type; TIGR4 spxB lctO double mutant compared to wild type was non-significant.