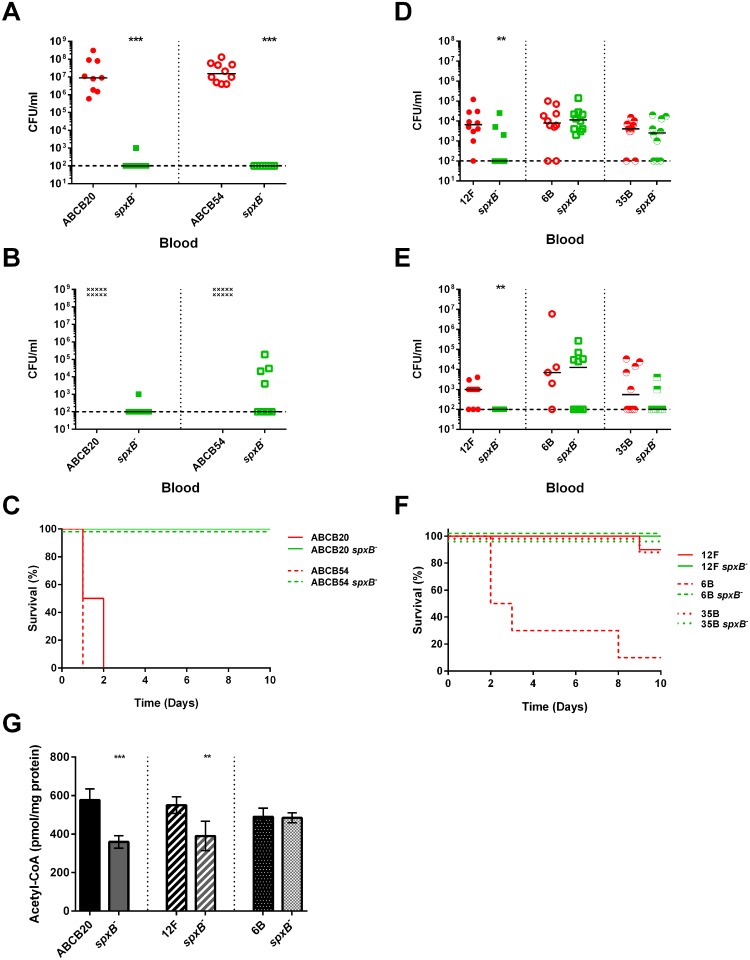
Fig 12. Deletion of spxB attenuates virulence and reduces steady-state acetyl-CoA in other pneumococcal strains with acetylated capsules.
BALB/c mice were infected IP with 5 x 104 cells. Bacterial presence in the blood in mice in strains with type 4 capsule was determined at 24 hours (A) and 48 hours (B) post infection and survival of mice was followed for 10 days (C). For strains with other capsule type—12F, 35B, 6B—bacterial presence in the blood in mice was determined at 24 hours (D) and 48 hours (E) post infection and survival of mice was followed for 10 days (F). Mice that did not survive to the 48 hour blood titer count are denoted by the symbol (x). Acetyl-CoA levels were measured in the wild type and spxB mutant in ABCB20, 12F, and 6B backgrounds (G). For each time-point of bacterial titers, mutant strains were compared to wild type using nonparametric Mann-Whitney t test; ** p = 0.01–0.001, *** p< 0.001. Survival data were analyzed using the Mantel-Cox log rank test. p< 0.0001 for ABCB20, ABCB54, and 6B spxB mutants compared to wild type; 12F and 35B spxB mutants compared to the wild type were non-significant. Acetyl-CoA values were normalized to total cellular protein and then plotted as pmol/ mg protein. The mutant was compared to the wild type using unpaired parametric t test; ** p = 0.01–0.001, *** p< 0.001.