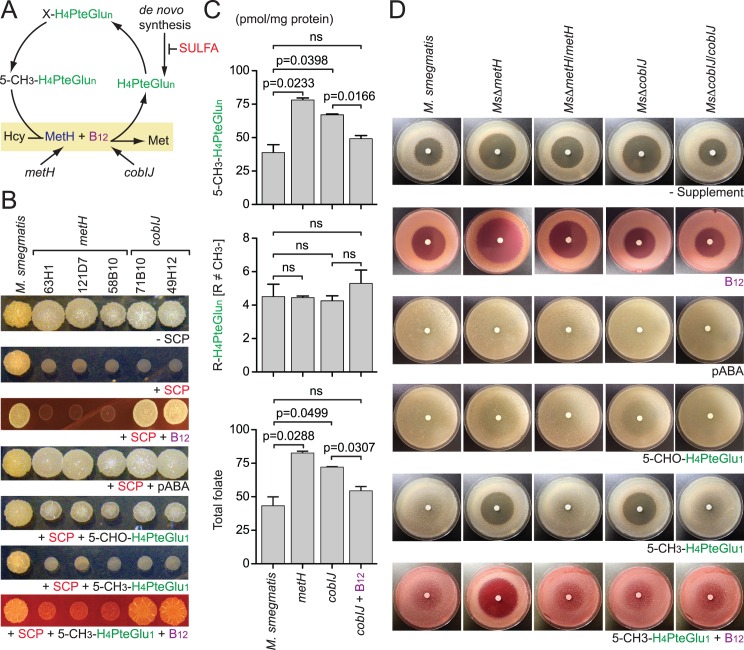
Fig 2. Methylfolate trap in Mycobacterium smegmatis.
(A) A model depicting the chemical conversions and factors involved in the methylfolate trap-mediated SULFA sensitivity. The CH3- group in 5-CH3-H4PteGlun is first transferred to the B12 cofactor, which further transfers it to homocysteine (Hcy) to make methionine (Met). The MetH reaction thereby recycles 5-CH3-H4PteGlun back to free H4PteGlun which continues the flow of the one-carbon network. (B) Chemical complementation of M. smegmatis “white” mutants mapped to metH or cobIJ. The strains exhibited increased SULFA susceptibility and impaired 5-CH3-H4PteGlu1 utilization. Approximately 5x103 cells were spotted onto NE medium added with 10.5 μg/ml SCP with or without exogenous supplements. Unlike wild type and other mutants, these mutants were unable to use 5-CH3-H4PteGlu1 to antagonize SCP. Exogenous B12 restored 5-CH3-H4PteGlu1 utilization and SCP resistance to cobIJ but not metH mutants. (C) Effect of metH and cobIJ on the folate pool in M. smegmatis. Growing cultures of M. smegmatis strains were treated with 285 μg/ml SCP for 30 min followed by folate extraction and LC-MS/MS analysis. Data shows the combined levels of all 5-CH3-H4PteGlun species (top), all non-methyl folate species (middle), and the total folate (bottom). Bars represent means of biological triplicates with standard deviations. P values are shown above the bars and were calculated using unpaired Student’s t-test; ns, no significant difference between the indicated strains. (D) Targeted mutagenesis confirms the roles of metH and cobIJ in methylfolate trap-induced SULFA sensitivity and 5-CH3-H4PteGlu1 utilization in M. smegmatis. Paper discs were embedded with 0.5 mg SCP and placed at the center of the medium surface, seeded with bacterial strains. Exogenous B12 and 5-CH3-H4PteGlun were used at 0.3 and 1 mM, respectively. Genetic complementation was achieved by in trans expression of metH or cobIJ. B12 alone restored wild type SULFA resistance level to MsΔcobIJ, whereas the combination of 5-CH3-H4PteGlu1 and B12 completely abolished SULFA resistance to all strains but MsΔmetH.