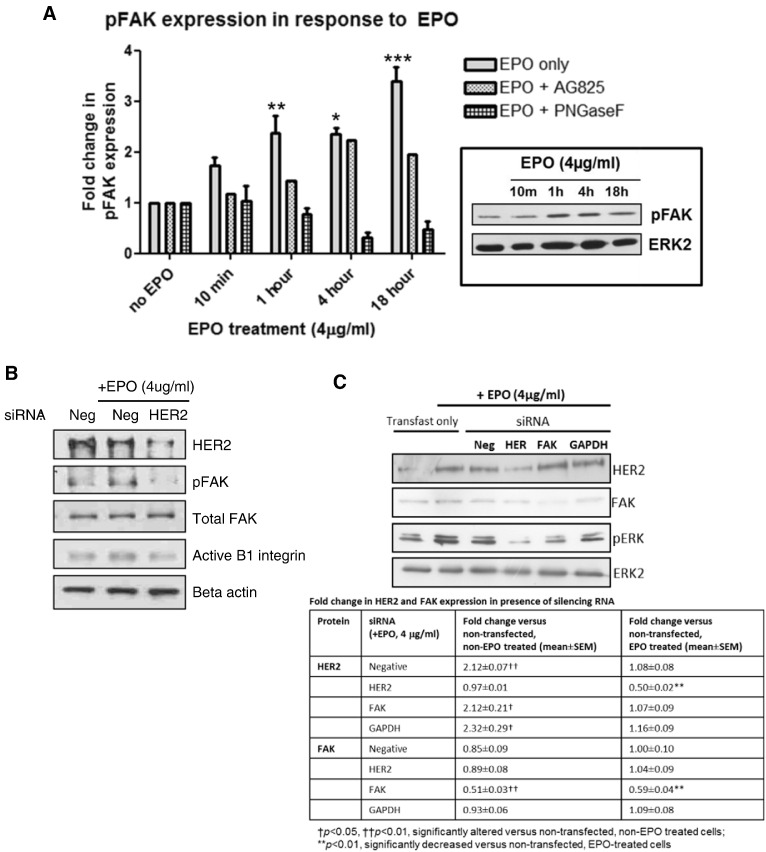
Fig. 5.
EPO induces the activation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and HER2 which are required for activation of β1 integrin
(A) Western blots of 16HBE14o protein from cells treated with or without EPO (4 μg/ml) at the indicated times. Some were pre-treated with the inhibitor AG825 (10 μM, 2 h) or the endoglycosidase PNGase F (2 U/ml, 1 h) (see legend) and probed with a rabbit anti-human pFAK antibody. The graphs show the fold change in pFAK expression levels in response to EPO treatment compared to untreated cells in the absence or presence of inhibitors at the indicated times. (n = 3, mean ± sem; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). The blots shown are representative of 3 similar experiments. Protein levels of total FAK remain unchanged in the presence of EPO and the various inhibitors studied (data not shown). (B) Western blots of 16HBE14o cells grown in the absence or presence of EPO (4 μg/ml, 18 h) as indicated. Cells were transfected with silencing RNA (siRNA) to a scrambled negative control (Neg) or HER2. (C) Western blots of 16HBE14o cells grown in the absence or presence of EPO (4 μg/ml, 18 h) as indicated. Cells were transfected or not with siRNA to a scrambled negative control (Neg), HER2, FAK or GAPDH. Table shows the fold change in HER2 and FAK protein expression following transfection.