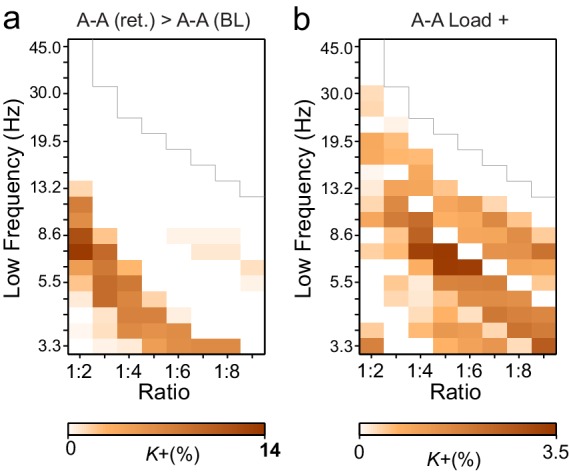
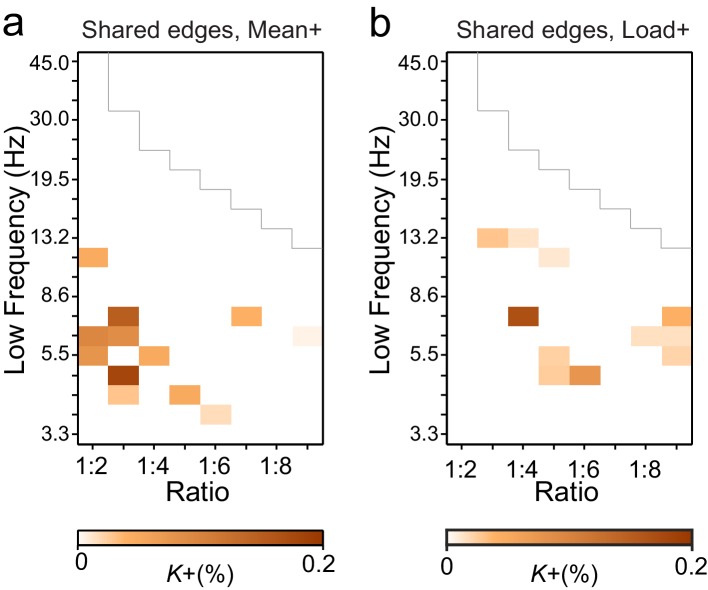
Figure 3. During VWM retention, inter-areal CFS was both strenghtened and suppressed in harmonic structures.
(a) Fractions (K+) of inter-areal CFS connections that were significantly stronger during VWM maintenance than in the pre-stimulus baseline (Mean condition, Wilcoxon signed ranked test, p < 0.05, corrected). K+ values (color scale) are shown for all studied pairs of 1:m ratios from 1:2 to 1:9 (x-axis) and lower frequencies from 3.3 to 45 Hz (y-axis) and represent data from an adjacency matrix for each frequency-pair. The grey line marks the boundary set by the highest investigated frequency (90 Hz). CFS of high-θ and high-α with their upper frequencies was increased for essentially all ratios. Right: The brown line indicates the harmonic consistency of CFS across low frequencies. The dashed line denotes the 95%-ile confidence limit. CFS of high-θ and high-α oscillations with their harmonics at higher frequencies is significantly consistent across ratios. (b) Fractions of inter-areal CFS connections (K-) that were suppressed below baseline levels during the retention period. Harmonic consistency (blue line) was estimated as in and shows that low-α consistent CFS was suppressed at all ratios.(c) Fractions of CFS connections that were significantly positively (K+) or (d) and negatively (K-) correlated with VWM load (Spearman Rank correlation test of CFS across the six VWM memory load conditions, p < 0.05, corrected).
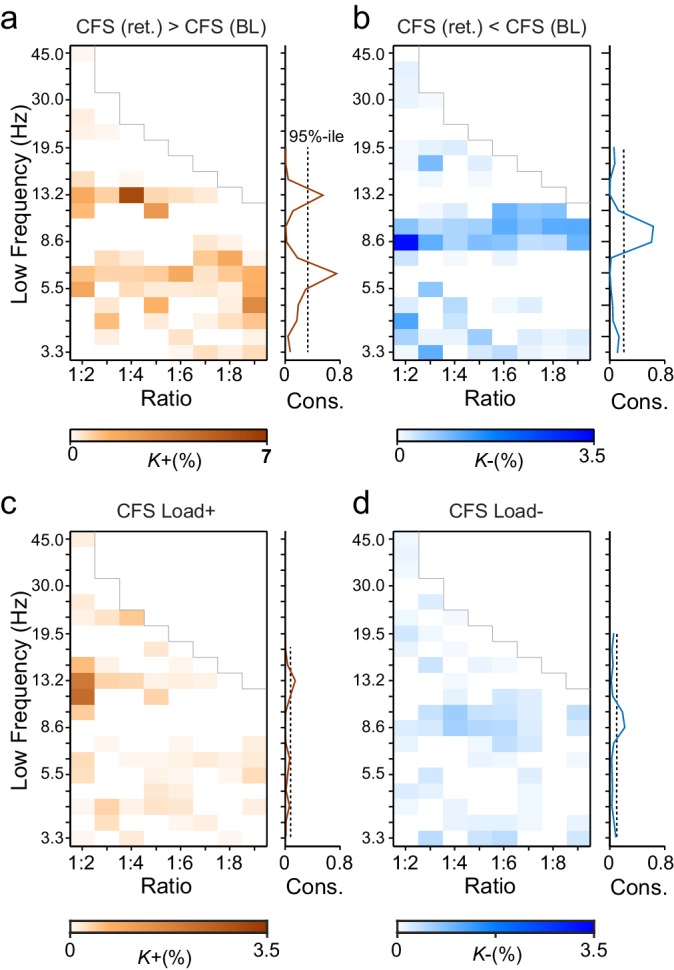
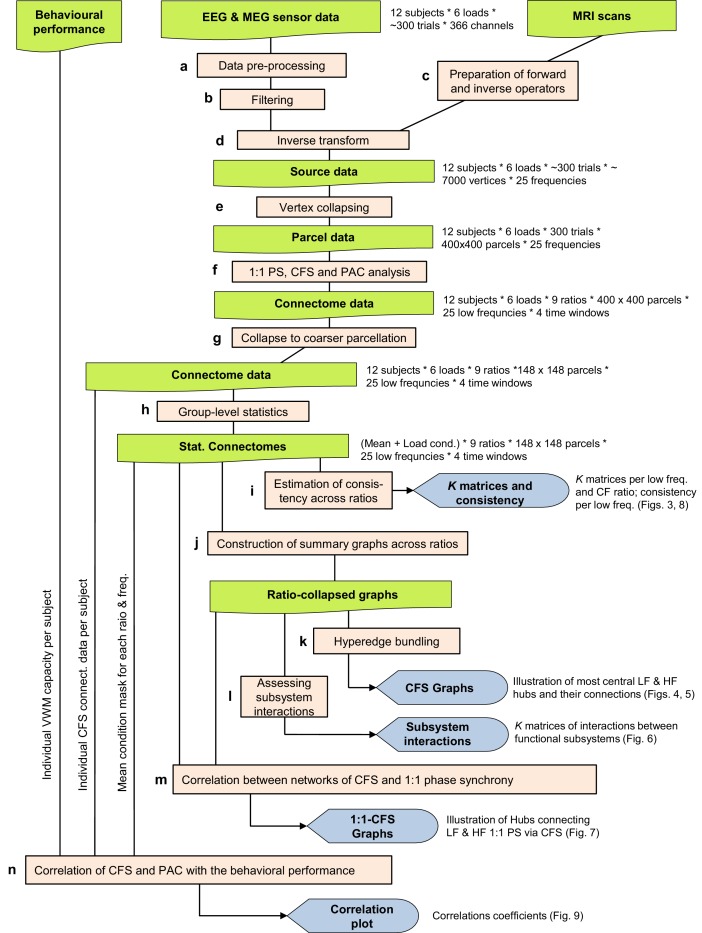
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Workflow.
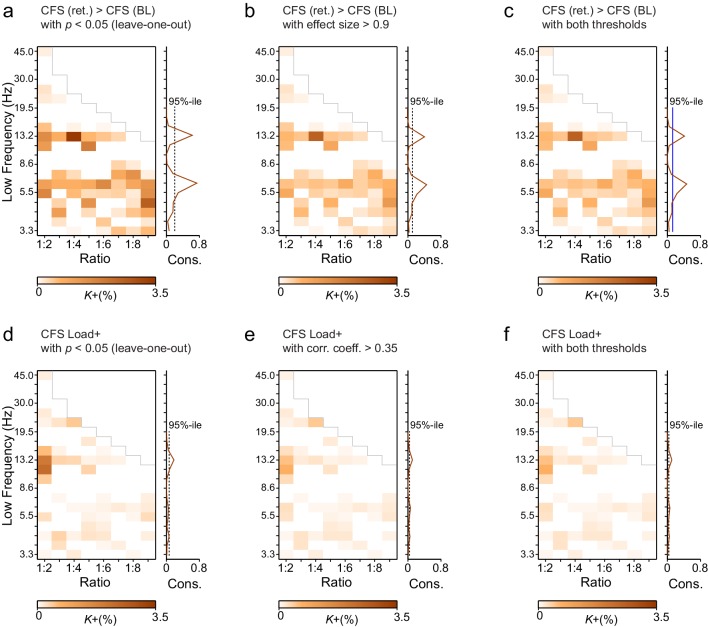
Figure 3—figure supplement 2. Leave-one-out statistics and effect size thresholding corroborate the robustness of CFS observations.
Figure 3—figure supplement 3. Apparent signal-to-noise ratio (aSNR) in source space.
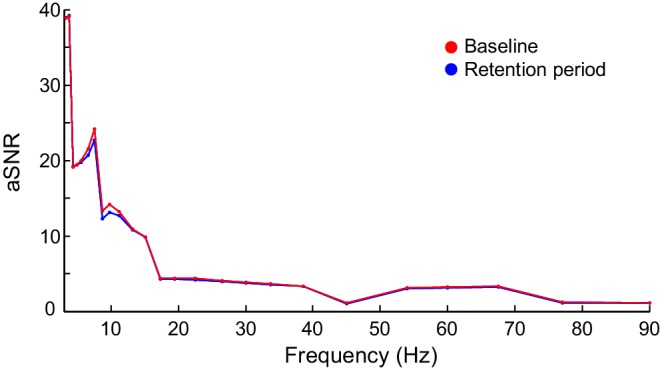
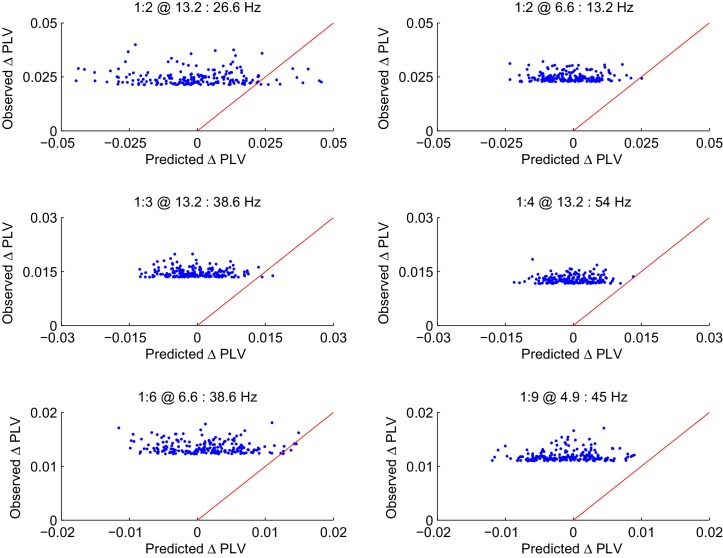
Figure 3—figure supplement 4. CFS PLV changes in the Mean condition are not attributable changes in the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR).
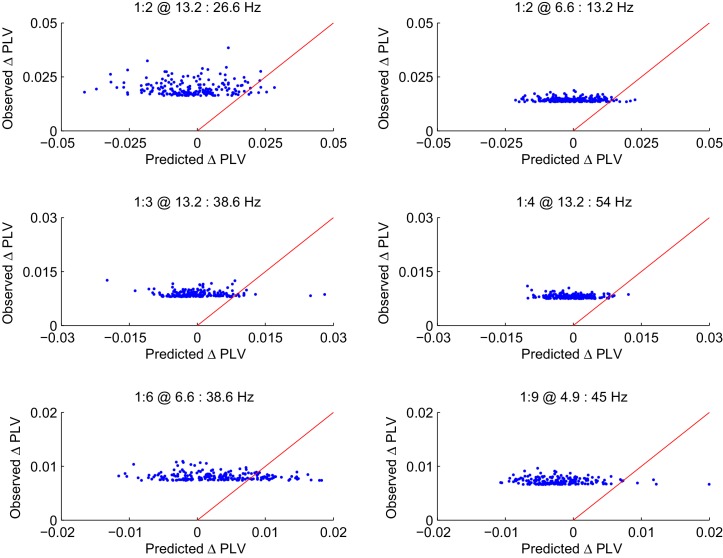
Figure 3—figure supplement 5. Observed PLV changes in the Load condition are not predicted by changes in SNR.
Figure 3—figure supplement 6. Changes in PLV and amplitude are not correlated.
Figure 3—figure supplement 7. Cross-frequency (CF) amplitude-amplitude correlations do not have a low-frequency consistent harmonic structure.