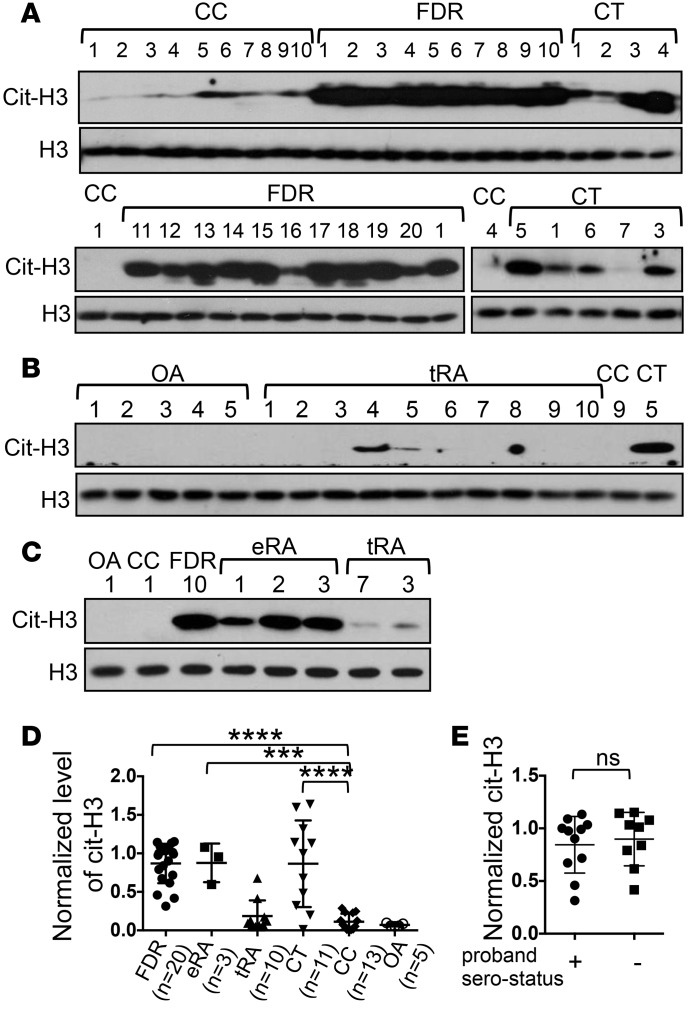
Figure 1. Hypercitrullination in PBMCs of healthy first-degree relatives of rheumatoid arthritis patients recruited at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
PBMCs obtained from healthy first-degree relatives (FDRs) (A), healthy donors carrying (CT) or not carrying (CC) the C1858T SNP (A and B), patients with osteoarthritis (OA) (B), treated rheumatoid arthritis (tRA) patients (B), and early/untreated rheumatoid arthritis (eRA) patients (C) were directly analyzed by Western blots for the level of citrullinated histone H3 (cit-H3) or total histone H3 (H3). The identity of each donor within each group is denoted with Arabic numerals. The level of cit-H3 was quantified with densitometry and normalized against that of H3. The normalized density of CT #4 in A was arbitrarily set as 1. The normalized density of cit-H3 from all donors is shown in D. The normalized cit-H3 levels of FDR of anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA+) or ACPA– probands are shown in E. Statistical analysis was performed with 1-way ANOVA followed by multiple comparison tests (D) or with 2-tailed Student’s t test (E). The CC group was used as the control group. ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. The bars shown in D and E represent mean ± SD.