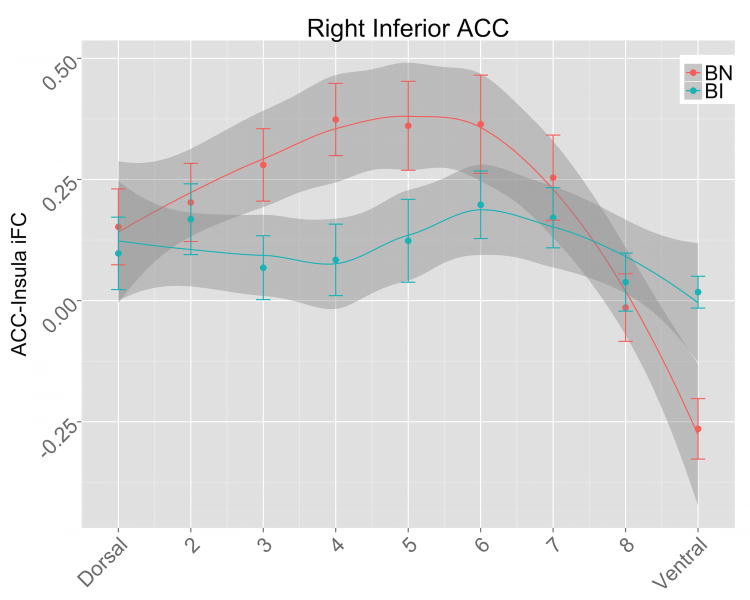
Figure 1.
Insula-ACC iFC patterns. In BN children (blue), there is a curvilinear pattern of right inferior ACC connectivity to the insula—iFC increases to a peak in the mid-dorsal ACC, and then drops for ventral ACC (which extends to sub-genual ACC/vmPFC). The topographical pattern of iFC in inferior ACC is disrupted in BI children (red), who for both right and left inferior ACC show a more linear dorsal-ventral topography, lacking the mid-dorsal peak and negative vmPFC iFC that is prominent in the BN group (note non-overlapping 95% confidence intervals shaded in gray in dACC and vmPFC). Lines: smoothed (LOESS) curve of insula iFC for dorsal to ventral ROIs, for BI and BN groups, with 95% confidence intervals in gray shading. The curves were generated in the R Statistics software using the ggplot package with the stats_smooth function. LOESS modeling has the advantage of not assuming a specific function (e.g., linear, quadratic) in the topographic pattern of insula-anterior cingulate connectivity, which is unknown and may vary between groups. The resulting LOESS curve and 95% confidence intervals for each group reveal regions where the groups' pattern of iFC differs. Points: group mean insula iFC for each ACC ROI, with error bars for 1 standard error of the mean.