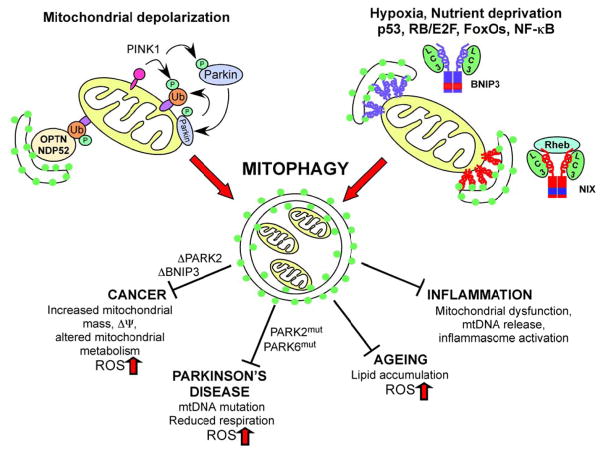
Figure 1. Schematic illustrating mechanisms and role of mitophagy in disease.
PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy promotes elimination of depolarized mitochondria through the concerted action of PINK1 kinase on ubiquitin and the Parkin E3 ubiquitin ligase that is recruited by PINK1 to the outer mitochondrial membrane where it ubiquitinates substrates such as Mitofusin-2 and VDAC1. The actions of BNIP3 (blu ue) and NIX (red) are induced by stress signals downstream of hypoxia, nutrient deprivation and specific developmental cues. Both BNIP3 and NIX function as homo-dimers at the OMM and interact directly with processed LC3 at phagophore membranes to promote mitochondrial turnover. The interaction of NIX with LC3 and its mitophagy functions are stimulated by interaction with Rheb. Defects in mitophagy contribute to cancer, Parkinson’s disease, ageing and inflammation amongst other diseases as a result of mitochondrial dysfunction, increased ROS production, mtDNA mutation, reduced respiration, altered metabolism and other adverse consequences of the loss of this important mitochondrial quality control mechanism.