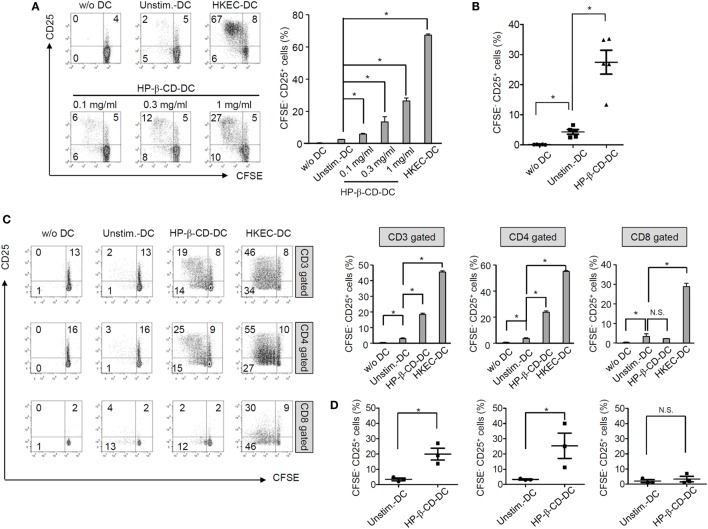
Figure 2.
HP-β-CD-sensitized DCs elicit the proliferation and activation of autologous T lymphocytes. Human monocyte-derived DCs (2.5 × 105 cells/ml) were stimulated with HP-β-CD (0, 0.1, 0.3, or 1 mg/ml) for 16 h. Then, the cells (5 × 104 cells) were cocultured with CFSE-labeled autologous CD3+ T cells (5 × 104 cells) for 4 days. (A) T lymphocyte proliferation and CD25 expression were analyzed by flow cytometry. The bar graph beside the histograms displays the average of triplicate measurements for the proliferation of CD25+ T lymphocytes. (B) A scatter plot indicates activated T lymphocytes by DCs (n = 5). (C) The proliferation and CD25 expression levels of CD3+, CD4+, or CD8+ T lymphocytes were analyzed by flow cytometry. The bar graphs on the right side of the histograms exhibit the average of triplicate measurements for the proliferation of CD25+ T lymphocytes. (D) Scatter plots exhibit activated CD3+, CD4+, or CD8+ T lymphocytes by DCs (n = 3). The immune responses of T lymphocytes cultured with HKEC-stimulated DCs are shown as positive controls. The numbers on the histograms indicate the percentages of T lymphocytes in each quadrant. *P < 0.05. Unstim.-DC indicates T lymphocytes cocultured with unstimulated DCs.