FIGURE 1.
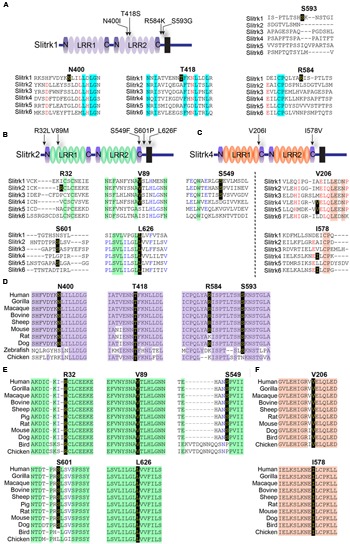
Alignment and conservation across different species of Slitrk1, Slitrk2, and Slitrk4 (Slit- and Trk-like) residues that are mutated in human patients with schizophrenia, Tourette syndrome, or trichotillomania. (A–C) Alignment of human Slitrk amino acids surrounding the mutated residues found in human patients with neuropsychiatric disorders. The target mutated resides are indicated in bold. Schematic drawings of the entire domain organization of human Slitrk1 (A), Slitrk2 (B), and Slitrk4 (C) are shown. (D-F) Similarity or identity of mutated residues investigated in the current study was determined by analyzing the amino acid sequences of human Slitrk1 (D), Slitrk2 (E), and Slitrk4 (F) deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database. Identical residues across various species are indicated in yellow letters on a black background. The following GenBank accession numbers were utilized for sequence alignment: Slitrk1/human, NP_443142; Slitrk1/gorilla, XP_004054683; Slitrk1/macaque, NP_001247716; Slitrk1/bovine, XP_002691955; Slitrk1/sheep, XP_004012247; Slitrk1/mouse, EDL00537; Slitrk1/rat, NP_001100753; Slitrk1/dog, XP_542628; Slitrk1/zebrafish, XP_687093; Slitrk1/chicken, XP_416993; Slitrk2/human, NP_001137482; Slitrk2/gorilla, XP_004065021; Slitrk2/macaque, NP_001248149; Slitrk2/bovine, XP_015325702; Slitrk2/sheep, XP_004022343; Slitrk2/pig, XP_013841934; Slitrk2/rat, NP_001101057; Slitrk2/mouse, AAI12407; Slitrk2/dog, XP_013967295; Slitrk2/bird, XP_012428589; Slitrk2/chicken, XP_420364; Slitrk4/human, NP_001171679; Slitrk4/gorilla, XP_004065019; Slitrk4/macaque, XP_001086308; Slitrk4/bovine, XP_005227618; Slitrk4/sheep, XP_004022346; Slitrk4/rat, NP_001100417; Slitrk4/mouse, AAI17892; Slitrk4/dog, XP_005641950; Slitrk4/bird, XP_012428616; and Slitrk4/chicken, XP_015134020.
