FIGURE 4.
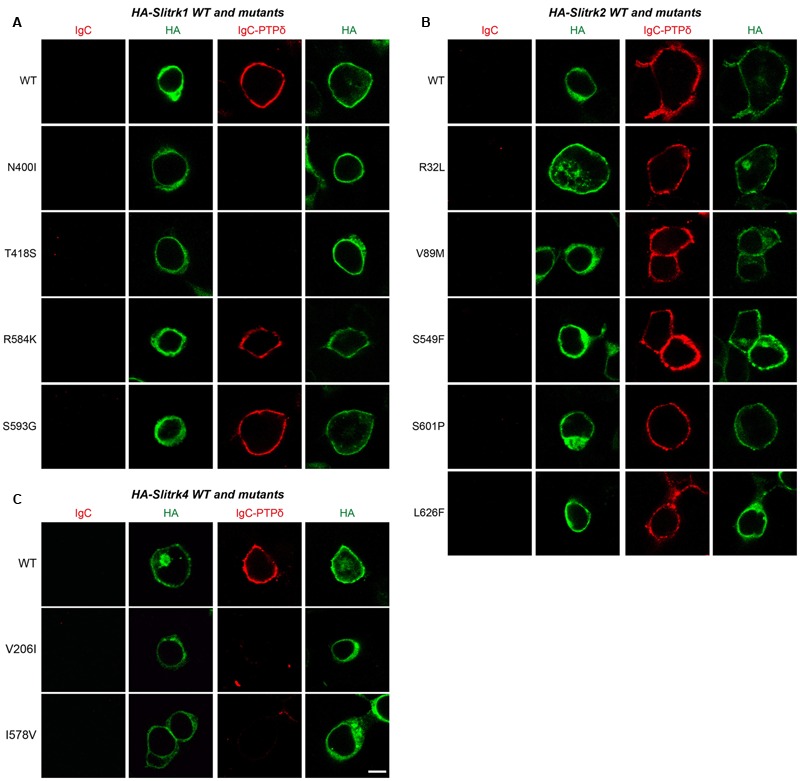
Characterization of LAR-RPTP–binding properties of Slitrk mutations. Representative images of cell-surface–binding assays. HEK293T cells expressing WT or mutant forms of HA-tagged Slitrk1 (A), Slitrk2 (B), or Slitrk4 (C) were incubated with 10 μg/ml control IgC or Ig-PTPδ, and then analyzed by immunofluorescence imaging of Ig-fusion proteins (red) and HA antibodies (green). Percentages of the cells exhibiting the binding of Ig-PTPδ were as follows: WT Slitrk1, 66.7%; Slitrk1[N400I], 32%; Slitrk1[T418S], 41%; Slitrk1[R584K], 62%; Slitrk1[S593G], 68.7%; WT Slitrk2, 71%; Slitrk2[R32L], 82%; Slitrk2[V89M], 81%; Slitrk2[S549F], 68.8%; Slitrk2[S601P], 80%; Slitrk2[L626F], 76%; WT Slitrk4, 81%; Slitrk4[V206I], 24%; and Slitrk4[I578V], 22.2%. Note that a subset of Slitrk mutants (Slitrk1[N400I], Slitrk1[T418S], Slitrk4[V206I] and Slitrk4[I578V]) exhibit reduced binding to Ig-PTPδ, paralleling their impaired surface transport (see Figure 3). Scale bar, 10 μm (applies to all images).
