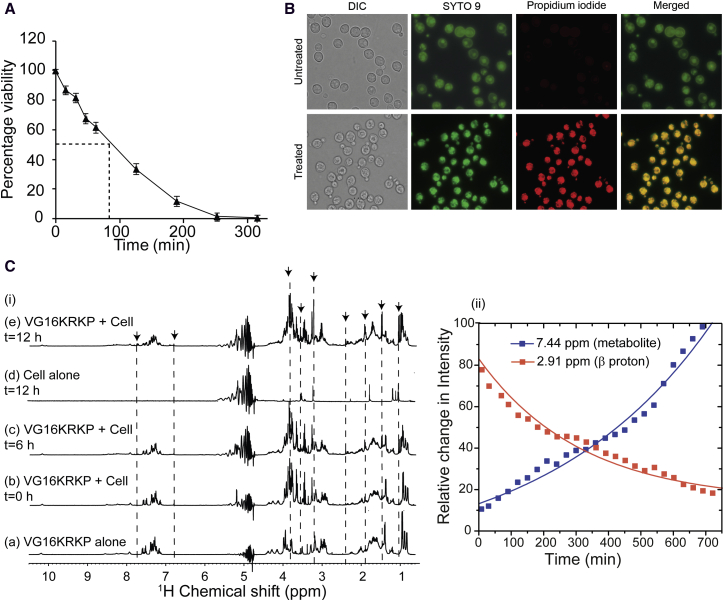
Figure 1.
Killing kinetics of Cryptococcus upon treatment with VG16KRKP. (A) Time kill curve of C. neoformans upon treatment with VG16KRKP. (B) Fluorescence-based live-dead staining to show the differentially stained cells after treatment with the peptide. The treated cells are stained with both SYTO9 and PI whereas untreated cells are only stained with SYTO9 but not with PI. (C) (i) 1D 1H proton NMR spectra of VG16KRKP alone (a); VG16KRKP upon addition of C. neoformans cells at different time points (b, c, and e) and C. neoformans cell alone incubated for 12 h (as control) (d). The spectrum of VG16KRKP in the presence of cell shows line-broadening effects, without changing the chemical shift, indicating the binding of the peptide to the cells. In contrast, appearance of new peaks in the spectrum in either the presence or absence of peptide corresponds to release of cell metabolites from the cell. (C) (ii) Plot showing the decrease in peptide resonance intensities (CβH protons of VG16KRKP) and at the same time increase in metabolite resonance intensities indicating binding and membrane disruption, respectively. To see this figure in color, go online.