Figure 7.
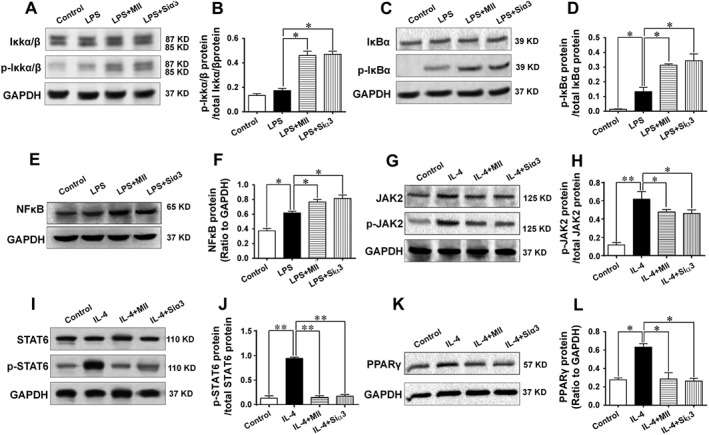
Mechanisms involved in the effect of the α3‐nAChR antagonist α‐conotoxin MII on the inflammatory response in macrophages. (A–F) Mechanisms underlying the effect of α3‐nAChRs on the M1 type polarization of macrophages. The protein expressions of the IκKα/β, p‐IκKα/β (Ser176), IκBα, p‐IκBα (Ser32) and NFκB were detected after macrophages were stimulated with LPS to induce the M1 type polarization in the presence of MII or after cells were knocked down with the gene of the α3‐nAChR. (G–L) Mechanisms involved in the effect of α3‐nAChRs on the M2 type polarization of macrophages. The protein expressions of JAK2, phosphorylated‐JAK2 (Tyr1007), STAT6, phosphorylated‐STAT6 (Tyr641) PPARγ were detected after macrophages were stimulated with IL‐4 to induce the M2 type polarization in the presence of MII or after cells were knocked down with the gene of the α3‐nAChR. Siα3: small interfering RNA targeting the gene of the α3‐nAChR. Values are means ± SEM. Data were obtained from five separate experiments (n = 5). Significance of the difference between groups is indicated as follows: * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01.
