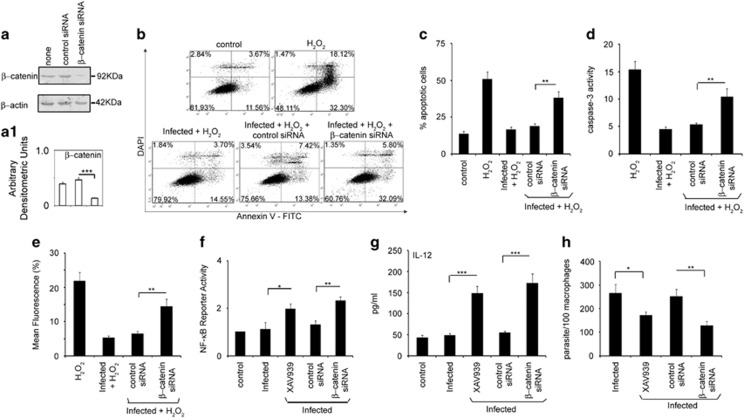
Figure 3.
Role of β-catenin in apoptois and inflammatory responses during infection. (a) RAW264.7 cells were transfected (24 h) with either control or β-catenin siRNA followed by infection with L. donovani promastigotes for 6 h. Expression of β-catenin was evaluated by immunoblot analysis. (b-e) Macrophages were transfected with β-catenin siRNA for 24 h, infected with L. donovani promastigotes for 6 h and then treated with 400 μM H2O2 for 1 h. These cells were then analyzed for the extent of apoptosis by annexin V-tagged FITC-DAPI flow cytometry after incubation for 24 h at 37 °C (b and c), caspase-3 activity using Ac-DEVDpNA as substrate (d) and mitochondrial integrity (e) as described in the legend of Figure 1. (f) RAW264.7 cells were treated with XAV939 (1 μM) or transfected with control or β-catenin siRNA along with pNF-κB luciferase plasmid (1 μg) and 0.5 μg of pCMV-β-gal. After 24 h of transfection, cells were infected with L. donovani promastigotes for 24 h, washed, lysed and processed for luciferase activity. (g and h) XAV939-treated or β-catenin siRNA transfected cells were infected with L. donovani promastigotes for 24 h and were processed for determination of IL-12 by ELISA (g) or estimation of extent of parasite survival (h). All experiments were repeated at least three times each and one set of representative data is shown. Bands were analyzed densitometrically and bar graphs expressing arbitrary densitometric units are presented adjacent to corresponding western blots. Error bars represent mean±S.D., n=3. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001; Student's t-test