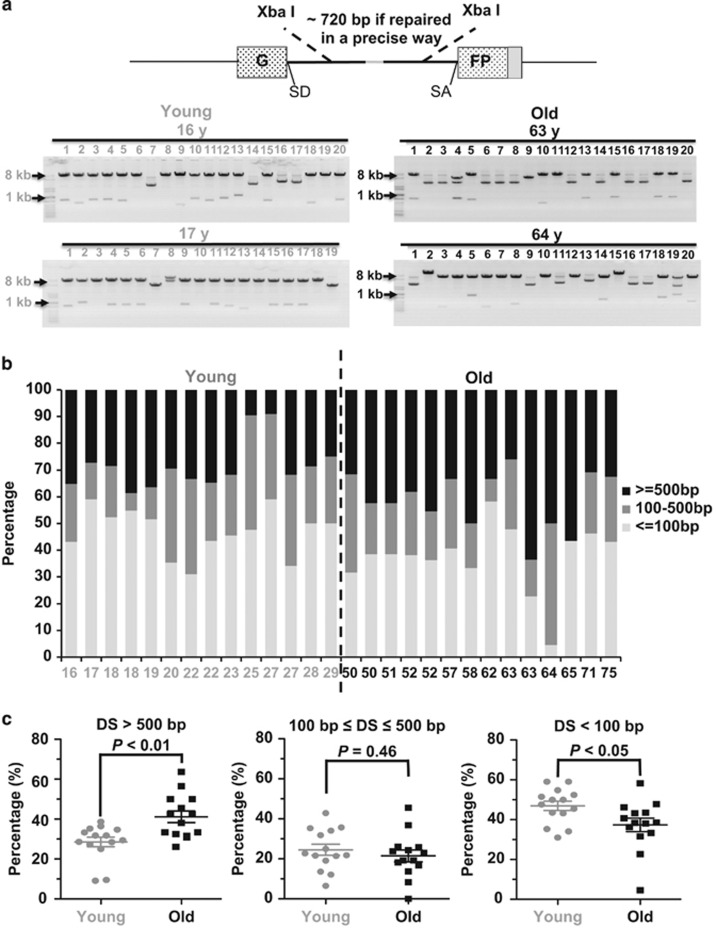
Figure 2.
NHEJ becomes more error-prone during aging. (a) A depiction of NHEJ fidelity analysis. At 72 h post transfection of 0.6 μg of linearized NHEJ construct into 106 cells, cells were collected for plasmid rescue. The rescued NHEJ plasmids were isolated and digested with XbaI restriction enzyme. Two XbaI recognition sites sit downstream and upstream of break sites, so the size of DNA bands after XbaI digestion would reflect the relative fidelity of NHEJ. Twenty rescued plasmids were isolated and digested with XbaI. Two representative gel pictures from two cell lines from each group are shown. (b) The frequency of acquiring different sizes of deletions in the 28 cell lines. For each cell line, at least 20 clones with deletions were sequenced at the junction areas. (c) The old group of cells are more likely to have large deletions but less prone to have small deletions than the young group of cells. The Mann–Whitney U (MWU) test indicates that the differences are significant. DS, deletion sizes