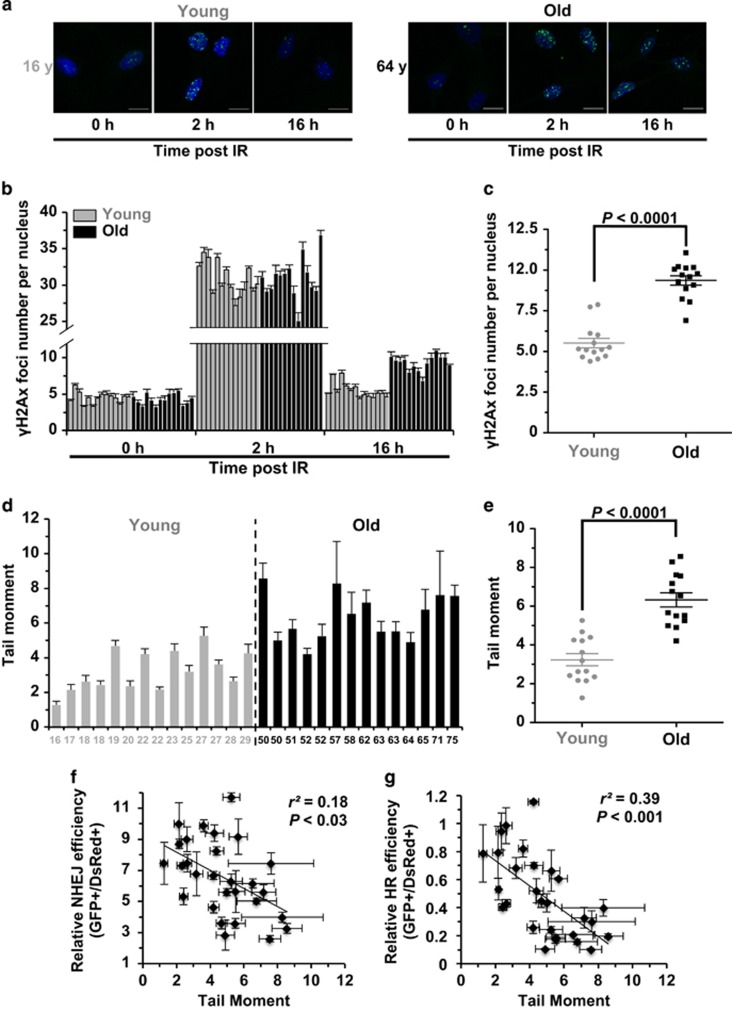
Figure 3.
Age-related decline of DNA DSB repair efficiency strongly correlates with genomic instability. (a) Representative pictures of γH2Ax foci at different time points post IR (X-ray, 8 Gy) in one young and old cell line. Scale bars, 10 μm. (b) Quantification of γH2Ax foci numbers at the three time points in the 28 cell lines. At least 50 cells were counted for each time points. Error bars, S.E.M. (c) Statistical analysis (MWU test) reveals that the old group of cells have a significantly higher number of γH2Ax foci at 16 h post IR than the young group of cells. (d) Comparison of genomic instability measured by neutral comet assay between the two groups. The 28 cell lines were analyzed at PD 16–19 using a kit from Trevigen. For each cell line, the tail moments of at least 50 cells were quantified using the Cometscore software (Sumerduck, VA, USA). Error bars, S.E.M. (e) MWU test reveals that the old group of cells have significantly higher tail moments than the young group. (f) There is a significant negative correlation between NHEJ efficiency and tail moment. Error bars of tail moment, S.E.M. Error bars of NHEJ efficiency, S.D. (g) There is a significant negative correlation between HR efficiency and tail moment. Error bars of tail moment, S.E.M. Error bars of HR efficiency, S.D.