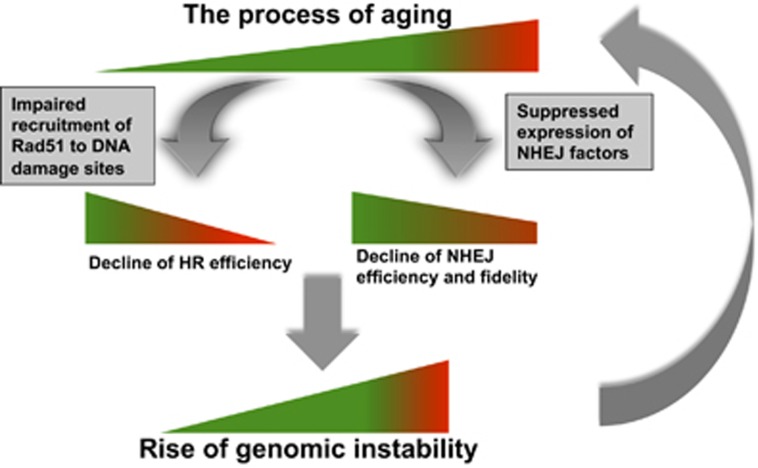
Figure 8.
Model for aging, change of DNA DSB repair and the rise of genomic instability. During the process of aging, the accumulation of mutations gradually impairs the recruitment of essential HR factors to DNA damage sites, and the expression of NHEJ factors, causing a decline o DNA DSB repair capacity. The age-related decline of HR is much shaper than that of NHEJ, possibly acting as a tumor suppressing mechanism. However, it also forces cells to choose the more error-prone NHEJ repair pathway. Decrease of both pathways eventually introduces more DNA mutations to genomes, leading to age-related to genomic instability, accelerating the process of aging