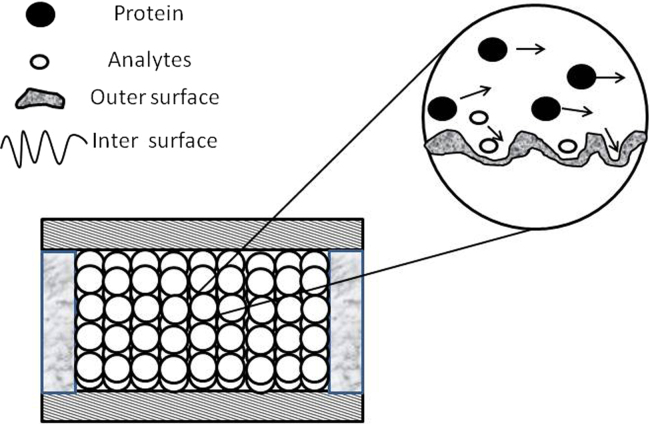
Figure 2.
Sketch of restricted access material material (RAM). Small molecules penetrate into the inner surface and are retained because of the hydrophobic effect, and thus matrix components of biological macromolecules are removed while the analytes are retained. Reprinted from Ref. 38 with permission of the copyright holder, Chinese Chemical Society.