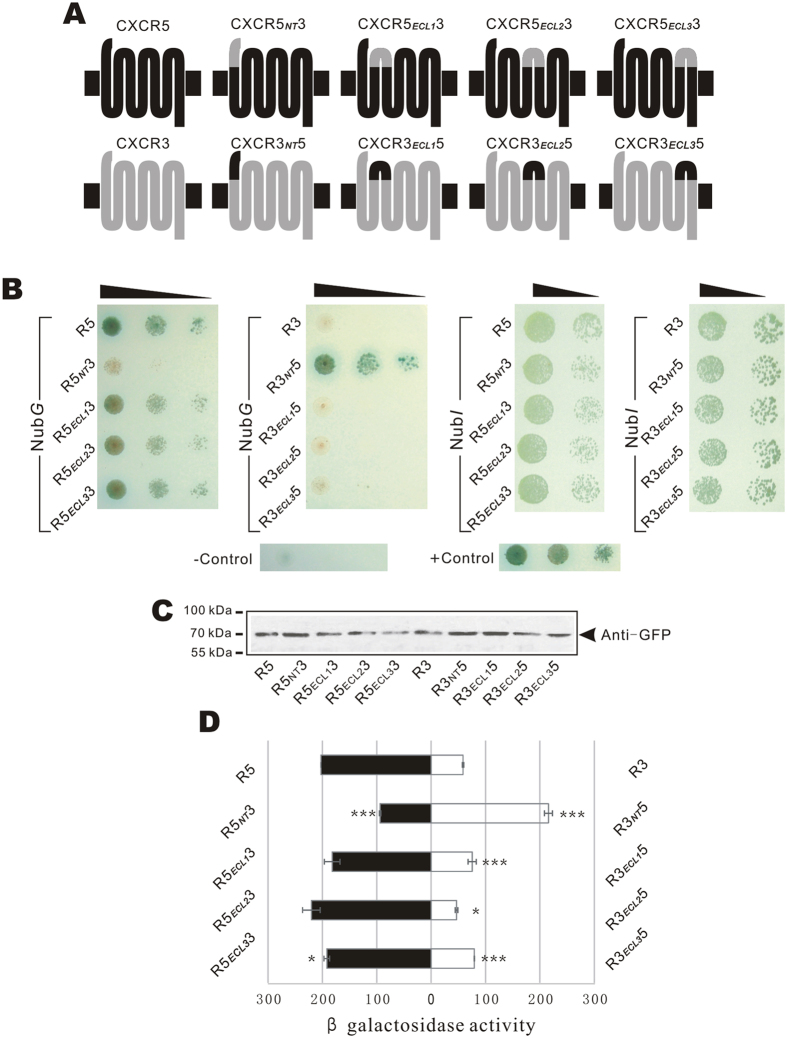
Figure 4. Detection of PPIs between CXCL12 and chimeric CXCR5.
(A) Structures of chimeric receptors of CXCR5 and CXCR3. Four extracellular fragments of CXCR5 were exchanged with counterparts of CXCR3 to form eight chimeric receptors. (B) Cell growth detection. Diploid cells expressing SPCXCL12-CXCL12-TMP-Cub-GAL4 and CXCR5-NubG, CXCR3-NubG, or NubG tagged chimeric receptors were detected by the growth ability on selection plate (SD-Leu−Trp−Ade−His−) with 15 mM 3AT + α-X-gal (left column). Diploid cells harboring the bait and NubI tagged preys were detected (right column). Positive and negative control cells were the same as Fig. 3B. (C) Expression detection by western blot assay. The chimeric preys labeled with EGFP were detected by western blot. (D) Quantitative β-Gal assay of diploid cells expressing SPCXCL12-CXCL12-TMP-Cub-GAL4 and NubG tagged chimeric receptors. The experiment was repeated three times independently and every sample was tested twice in each experiment (n = 2). * and *** indicate significance p < 0.05 and p < 0.001 of a t-test between chimeric receptors and wild-type counterparts.