FIG 2 .
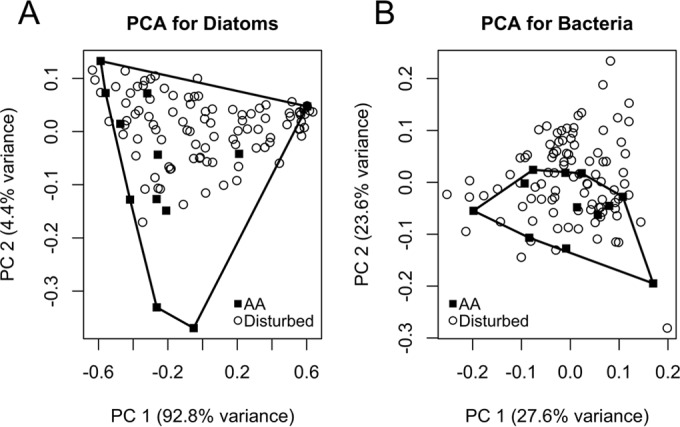
(A) Principal component analysis of the diatom communities showed that the undisturbed treatment, AA, spanned most of the space occupied by the communities in the nine treatments. The majority of disturbed communities fell within the bounds of the AA communities, showing a lack of separation between the AA treatment and the disturbed treatments. The first and second axes together account for 97.2% of community variation. The polygon depicted shows the convex hull of the AA points, which is constructed by drawing the minimum number of connections between points to encapsulate the entire set of AA points. (B) Results from the principal component analysis of the bacterial communities show that there is no strong differentiation between the community composition of the undisturbed treatment, AA, and that of the disturbed treatments. Additionally, the AA treatment covers a wide range of the PC 1 axis, which is the axis that explains the most variability between bacterial communities. The first and second axes together account for 51.2% of community variation. As above, the polygon depicted shows the convex hull of the AA points.
