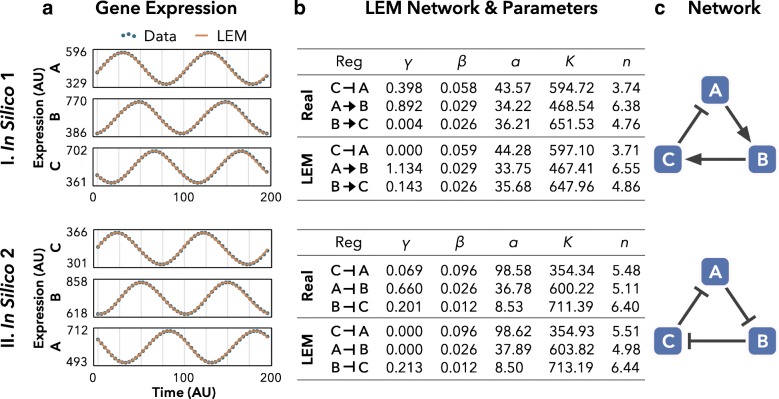
Fig. 2.
LEM recapitulates network structure and dynamics from time-series data. I, II Oscillatory gene expression data were generated in silico from three-node negative feedback networks (a, dotted lines). LEM uses ordinary differential equations to simulate the dynamics data for each node (a, solid lines). The parameters output from LEM closely approximate the parameters used to generate the data (b). LEM identifies the most probable regulation on each node, from which the user can generate a composite network diagram (c). The top regulations identified by LEM reconstruct the correct network topology for both networks (I in silico 1; II in silico 2). Out of a possible 39=19,683 topologies for three-node networks, LEM detects subtle differences in gene expression curve shapes to identify correctly a three-node negative feedback loop (I) and the repressilator [49] (II). AU arbitrary units, LEM Local Edge Machine