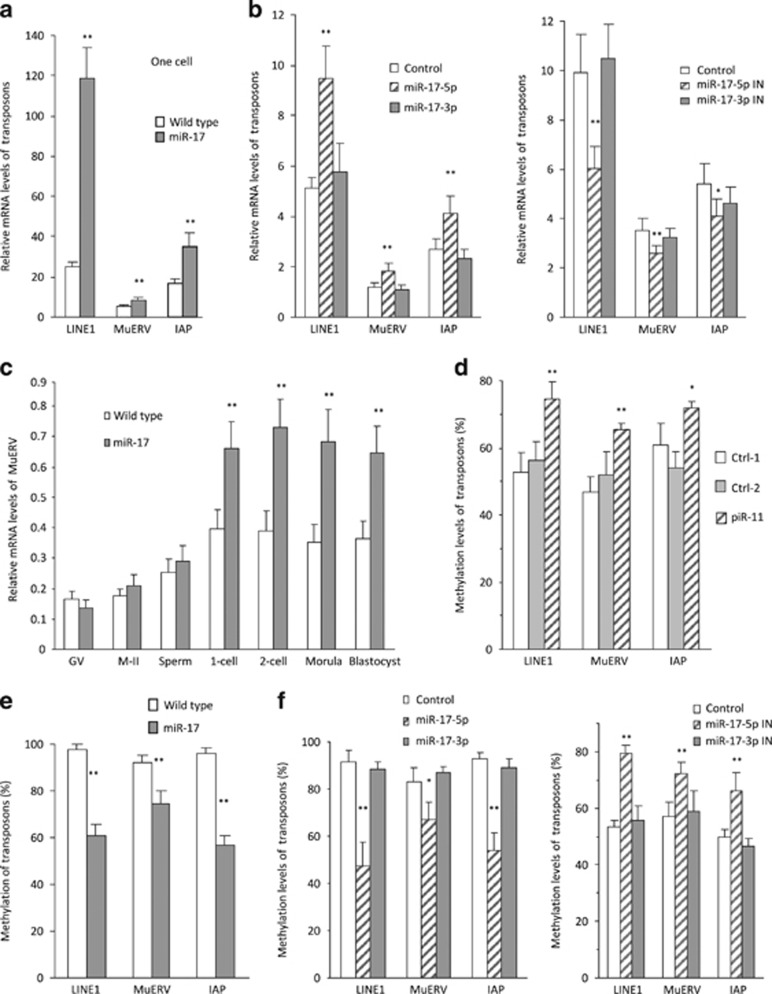
Figure 3.
Retrotransposons were derepressed in the early embryos of miR-17 transgenic mice. (a) Fifty zygotes were collected for RNA extraction, followed by real-time PCR. miR-17 transgenic zygotes expressed increased mRNA levels of retrotransposon LINE1, MuERV, and IAP. **P<0.01. Error bars, S.D. (n=4). (b) Wild-type zygotes were microinjected with miR-17-5p, miR-17-3p, and control oligos (left), or miR-17-5p inhibitor, miR-17-3p inhibitor, and control oligos (right), followed by incubation for 8 h and real-time PCR. Injection with miR-17-5p enhanced, but injection with miR-17-5p inhibitor inhibited levels of retrotransposon LINE1, MuERV, and IAP. *P<0.05. **P<0.01. Error bars, S.D. (n=4). (c) miR-17 transgenic embryos expressed increased mRNA levels of retrotransposon MuERV in zygote, two-cell, morula, and blastocyst stage. **P<0.01. Error bars, S.D. (n=4). (d) Hundred zygotes were collected for DNA extraction. Methylation-specific PCR (MSP) showed that piR11 injection increased methylation levels of retrotransposon LINE1, MuERV, and IAP. *P<0.05. **P<0.01. Error bars, S.D. (n=4). (e) MSP analysis indicated that methylation levels of retrotransposon LINE1, MuERV, and IAP decreased in the zygotes (100) isolated from miR-17 transgenic mice. **P<0.01. Error bars, S.D. (n=4). (f) MSP analysis indicated that methylation levels of retrotransposon LINE1, MuERV, and IAP decreased in zygotes injected with miR-17-5p (left), but increased in zygotes injected with miR-17-5p inhibitor (right). *P<0.05. **P<0.01. Error bars, S.D. (n=4)