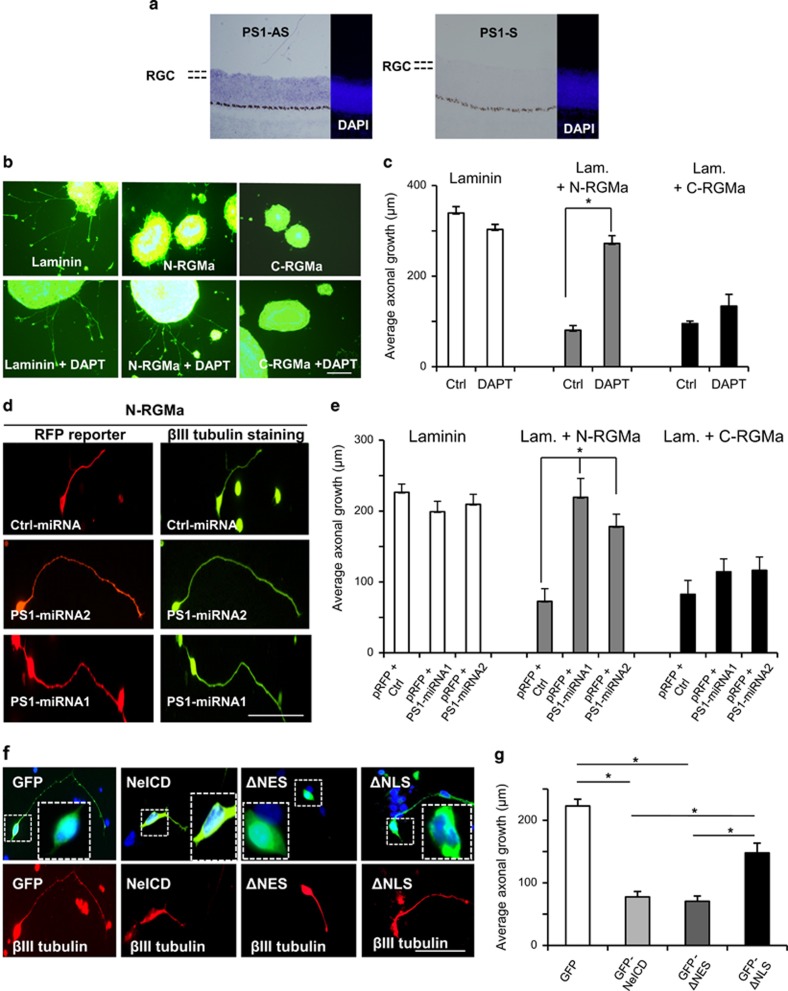
Figure 4.
ϒ-secretase and the intracellular domain of Neogenin (NeICD) mediate N-RGMa inhibition. (a) In situ hybridization with a presenilin-1 anti-sense (PS1-AS) probe demonstrated presenilin-1 expression by RGCs in the chick E8 retina. Negative control, sense (PS1-S). (b) RGCs explants were grown on RGMa peptides +/− ϒ-secretase inhibitor (DAPT). (c) Quantifications revealed that DAPT significantly suppressed the N-RGMa inhibition on growing axons. DAPT did not affect C-RGMa inhibition. (d) Temporal retinal cells were transfected with an RFP reporter together with an miRNA. RGC axons cultured on N-RGMa appeared longer in the presence of presenilin-1 (PS1) miRNAs. (e) Quantification showed that PS1-miRNA significantly restored outgrowth on N-RGMa (P<0.005). PS1-miRNAs did not affect outgrowth on either laminin or C-RGMa. (f) RGCs were transfected with (i) GFP, (ii) NeICD-GFP, or (iii) an NeICD-GFP mutant that lacks the nuclear export signal (ΔNES), or (iv) a mutant that lacks the nuclear localization signal of NeICD (ΔNLS). (g) Quantifications revealed that NeICD and ΔNES inhibited axonal growth to the same extent. ΔNLS significantly restored axonal growth when compared with NeICD and ΔNES (*P<0.001). Bars, 100 μm