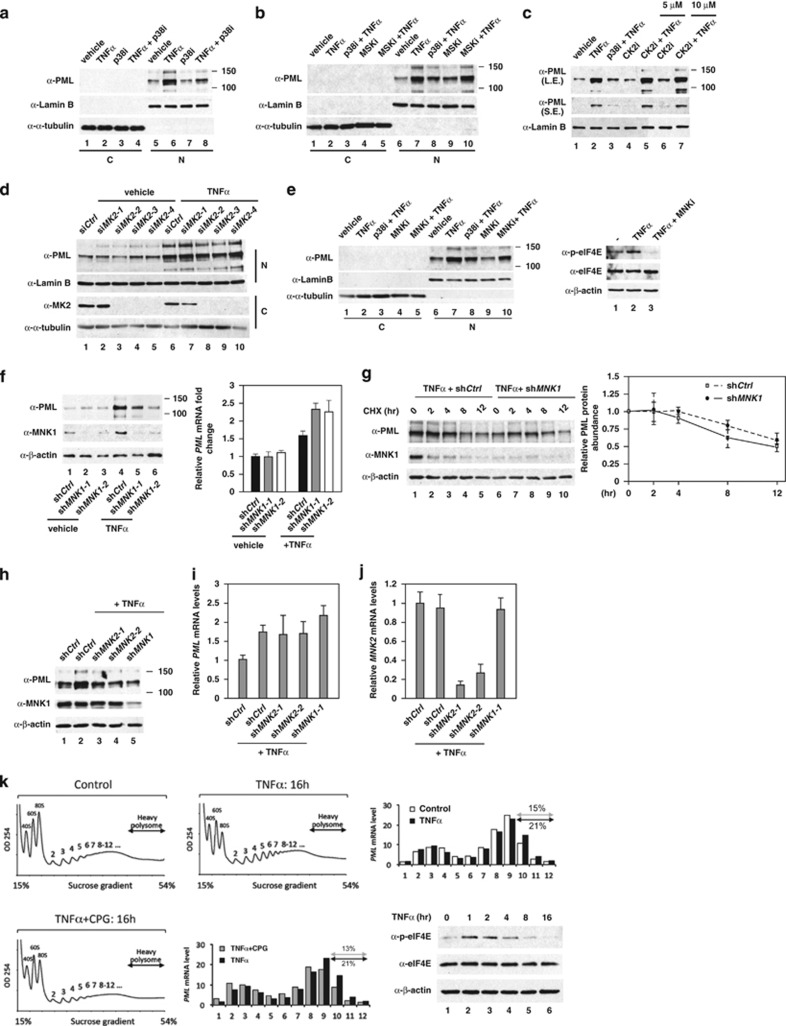
Figure 3.
MNKs are p38 downstream kinases that mediate TNFα-induced PML protein accumulation. HUVECs were pretreated with kinase inhibitors or transfected with kinase-specific siRNAs before TNFα treatment, followed by western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (a) HUVECs were treated with p38 kinase inhibitor and TNFα as indicated. Nuclear and cytosolic fractions were separated and subjected to western blotting. C: cytosolic fraction; N: nuclear fraction. (b) The effect of MSK inhibitor on TNFα-mediated PML protein accumulation in HUVECs. (c) The effect of CK2 inhibitor on TNFα-mediated PML protein accumulation in HUVECs. (d) The effect of knockdown of MK2 on TNFα-mediated PML protein accumulation in HUVECs. (e) The effect of a MNK inhibitor on TNFα-mediated PML protein accumulation in HUVECs. (f) The effect of knockdown of MNK1 on TNFα-mediated PML protein abundance and mRNA accumulation in HUVECs. The mRNA levels of PML in each sample were quantified by qRT-PCR (n=3). (g) Knockdown of MNK1 had little or no effect on PML protein half-life in TNFα-treated HUVECs. Quantitation of PML protein abundance from western blots is shown on the right (n=4). (h–j) The effect of knockdown of MNK2 on TNFα-mediated induction of PML protein in HUVECs. The mRNA levels of PML and MNK2 in each sample were quantified by qRT-PCR (n=3). (k) Polysome profiling analysis demonstrates that TNFα–MNK1 axis controls heavy polysome occupancy on PML mRNA