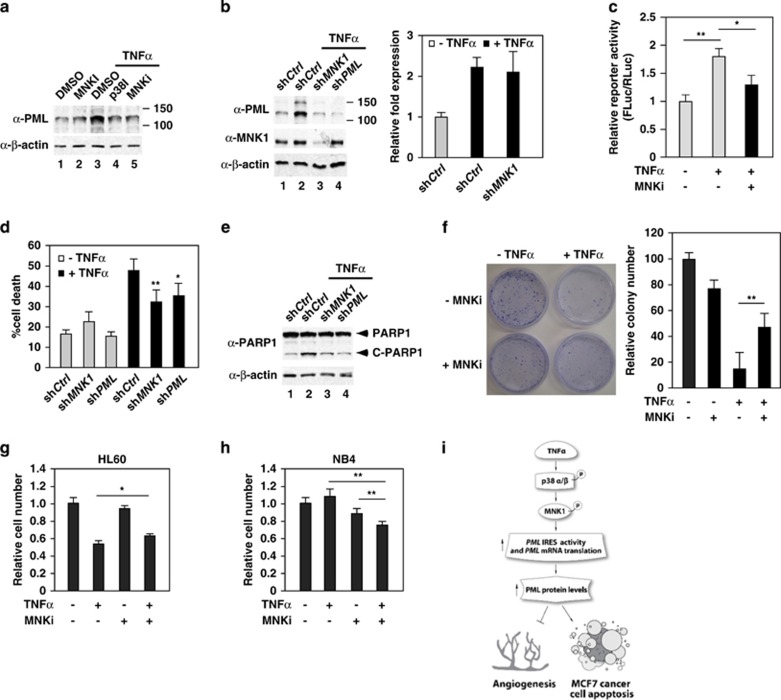
Figure 8.
MNK1 mediates TNFα-induced PML protein accumulation and apoptosis in MCF7 breast cancer cells. (a) The effect of inhibition of p38 and MNK1 activity on TNFα-induced PML protein expression in MCF7 cells. MCF7 cells were pretreated with kinase inhibitors followed by TNFα treatment, harvested, whole-cell lysates prepared and western blotted with the indicated antibodies. (b) The effect of knockdown of MNK1 on TNFα-induced PML protein and mRNA accumulation. (c) Inhibition of MNK1 activity reduces TNFα-mediated PML IRES activation in MCF7 cells. MCF7 cells were transiently transfected with PML 5′-UTR (-100->-1)-pRF plasmid for 72 h, treated with or without MNK1 inhibitor and TNFα and the cells were harvested. The relative activity of Firefly luciferase to Renilla luciferase was plotted as shown. The results are mean±S.D. in triplicates (n=3). (d and e) The effect of knockdown of MNK1 or PML on TNFα-mediated cell cytotoxicity in MFC7 cells (d) and the cleavage of PARP1 (e). MCF7 cells were infected with lentiviruses expressing a control, MNK1 or PML shRNA followed by TNFα treatment. Aliquots of cells were used to determine cell death rate by Trypan blue exclusion assays (d) or cleavage of PARP1 by western blotting (e). The results are mean±S.D. (n=6). (f) The effect of TNFα and the MNK1 inhibitor CGP57380 on TNFα-mediated inhibition of MCF7 cell proliferation determined by colony formation assays. (g and h) The effect of TNFα and the MNK1 inhibitor CGP57380 on TNFα-mediated cell cytotoxicity in HL60 and NB4 cells by WST-1 cell proliferation assays. (i) A model by which TNFα induces anti-angiogenesis and apoptosis activity through enhancing PML mRNA translation that involves PML IRES and the p38–MNK1 axis