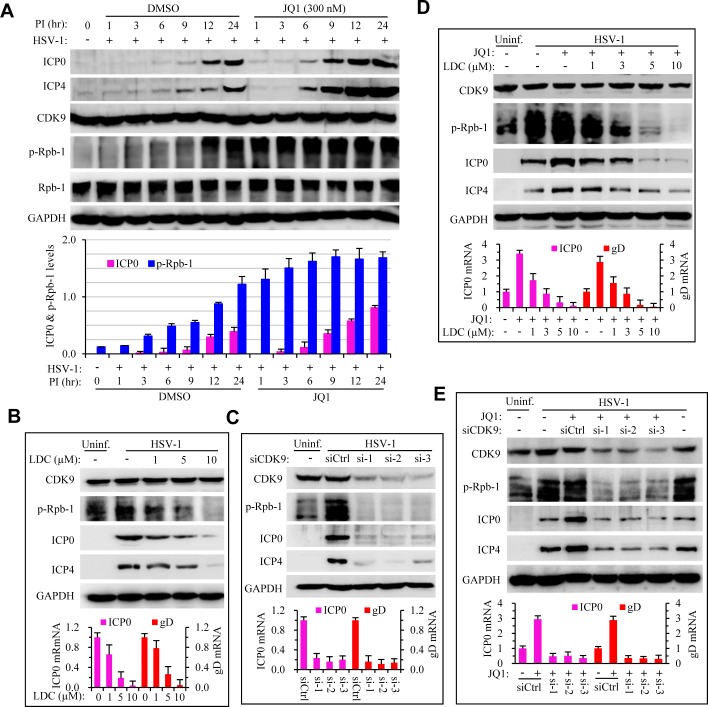
Fig 7. Requirement of CDK9 kinase activity for HSV-1 infection.
(A) JQ1 treatment promotes HSV-1 infection and increases the phosphorylation of Rbp-1/RNAP II. HeLa cells were infected with HSV-1 (1 MOI) in the absence or presence of 300 nM JQ1 for 24 hr. Protein expression and modification was determined using specific antibodies by immunoblotting. Lower panel bar graph represents quantitative measurement of ICP0 and phosphorylated Rpb-1 band intensities relative to GAPDH. (B) CDK9 inhibitor LDC000067 (LDC) dose-dependently blocks Rbp-1 phosphorylation (upper panels) and viral gene expression, determined by western blotting and qPCR, respectively. (C) Knock down of CDK9 expression blocks Rbp-1 phosphorylation and viral gene expression, determined by western blotting and qPCR, respectively. (D) CDK9 inhibitor LDC000067 (LDC) abolishes JQ1 effect on Rbp-1 phosphorylation and HSV-1 gene expression. (E) Knock down of CDK9 expression diminishes JQ1 effect on Rbp-1 phosphorylation and viral gene expression.