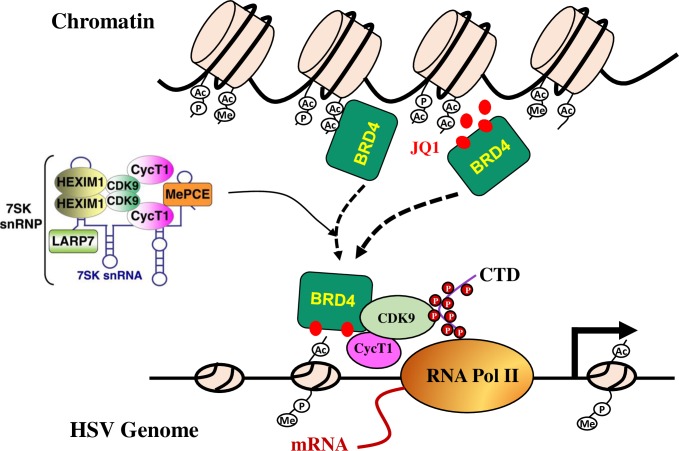
Fig 8. Model of BRD4 regulation of herpes simplex virus replication.
BRD4 participates in epigenetics regulation by recognition of acetyl lysine residues with its bromodomains (BD1, BD2). BRD4 also regulates the transcription of cellular and viral genes by recruitment of the positive transcription elongation factor (P-TEFb) and transcriptional factors. P-TEFb is itself under a stringent control by the inhibitory 7SK small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (7SK snRNP) complex. Infection by HSV-1 or HSV-2 causes BRD4 relocation and rededicates BRD4 and the protein complex to viral gene transcription. JQ1 (red dots) or BD1 domain proteins functions by dislodging BRD4 from chromatin association.