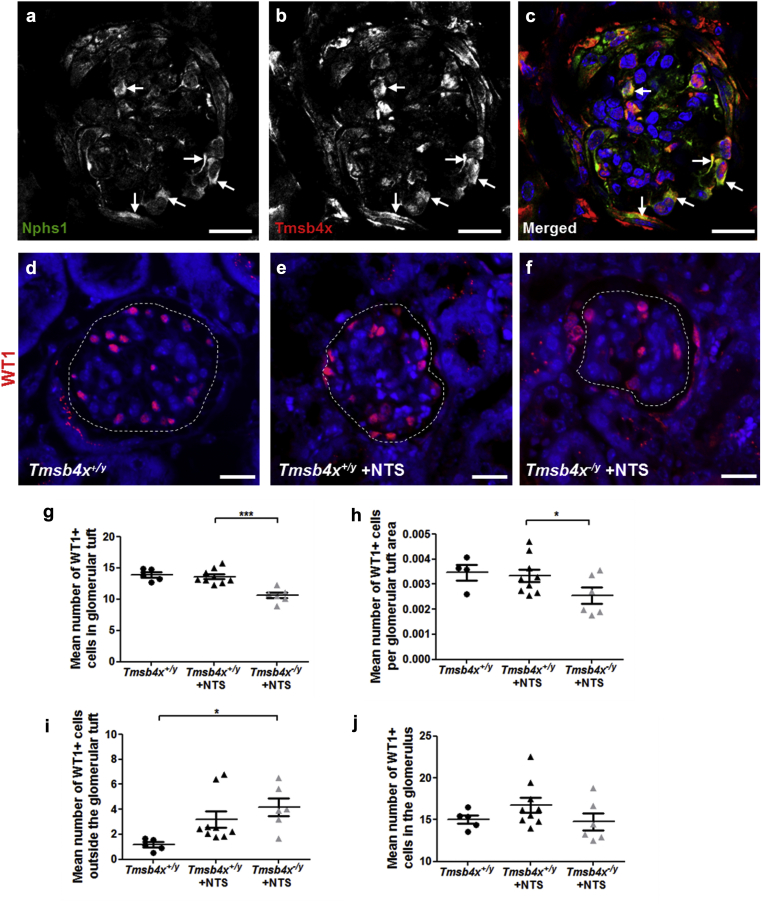
Figure 4.
Podocyte assessment in Tmsb4x+/yandTmsb4x−/ymice after induction of nephrotoxic nephritis. Representative image of nephrin (Nphs1; podocytes) (a) and Tmsb4x (b) staining in the adult wild-type mouse glomerulus 21 days after injection of nephrotoxic serum (NTS). Cells positive for both Nphs1 (green) and Tmsb4x (red) are indicated by arrows in the merged image (c). Representative images of glomeruli from Tmsb4x+/y (d), Tmsb4x+/y + NTS (e), and Tmsb4x−/y + NTS (f) mice stained for WT1. The glomerular tuft areas are indicate the dotted lines. (g–j) Graphs showing the number of WT1+ cells in the glomerular tuft (g), the number of WT1+ cells in the glomerular tuft normalized to the glomerular area (h), the number of WT1+ cells in the area of the glomerulus surrounding the glomerular tuft (i), and the number of WT1+ cells in the whole glomerulus (j). Cells were counted as 50 glomeruli per sample, except in (h), where cells were counted and normalized to the glomerular area as 15 glomeruli per sample. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Tmsb4x+/y (n = 5), Tmsb4+/y + NTS (n = 9), and Tmsb4x−/y + NTS (n = 6) mice. Bar = 20 μm. Tmsb4x, thymosin β4.