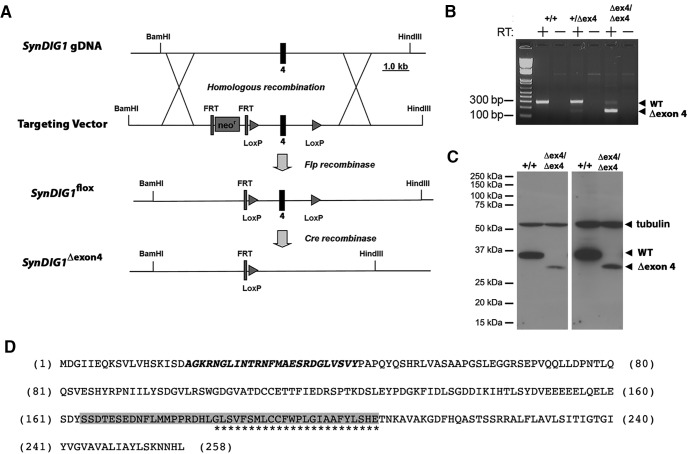
Figure 1.
Characterization of a conditional SynDIG1flox allele. A, Schematic of the conditional SynDIG1flox allele, which results in the removal of exon 4 (SynDIG1Δexon4) upon exposure to Cre recombinase. B, RT-PCR using purified tissue RNA from brain tissue of SynDIG1 wild-type (+/+), heterozygous (+/Δex4), and homozygous (Δex4/Δex4) mutant brains generated by crossing with Nes-cre transgenic mice detects the presence or absence of an mRNA lacking exon 4. A forward primer in exon 3 and a reverse primer in exon 5 produce a 295 or 138 bp product, respectively, in transcripts containing or lacking exon 4. Arrowheads indicate positions of WT and exon 4 lacking mutant products. Note that (+) refers to the unmodified unfloxed SynDIG1 allele. C, Chemiluminescence immunoblot to detect SynDIG1 expression in brain lysates from wild type (+/+) and homozygous (Δex4/Δex4) mutant animals generated by crossing with CMV-cre transgenic mice detects the presence or absence of SynDIG1 protein lacking amino acids encoded by exon 4. Arrowheads indicate full-length protein (WT), mutant protein (Δexon4), and tubulin (loading control) at 2 min (left) and 4 h (right) exposure times. Note that (+) refers to the unmodified unfloxed SynDIG1 allele. D, Amino acid sequence of full-length SynDIG1 protein. The epitope recognized by the anti-SynDIG1 antibody is within the region and is shown in bold italic type. Transmembrane amino acids are indicated by asterisks. Amino acids encoded by exon 4 that are eliminated in SynDIG1Δexon4 upon exposure to Cre recombinase are highlighted in gray.