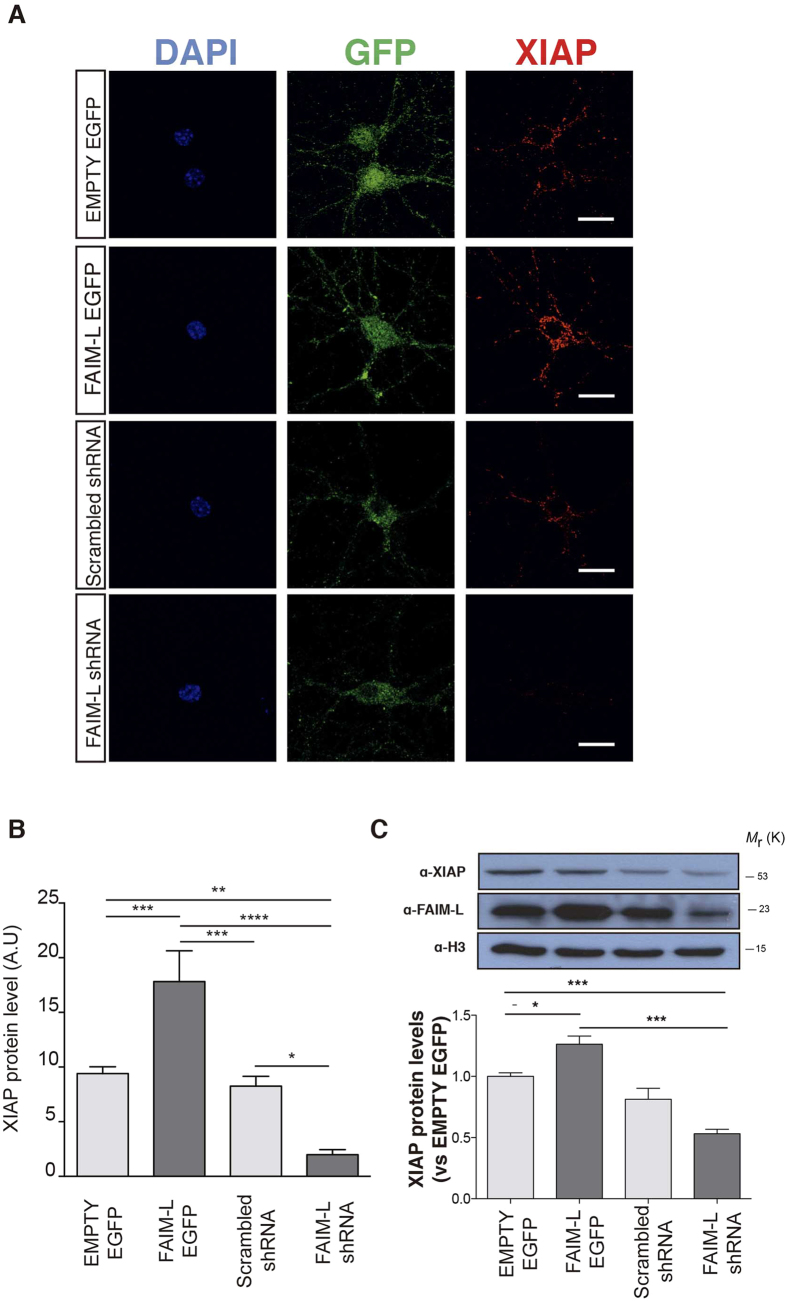
Figure 1. FAIM-L modulates the stability of XIAP protein levels in hippocampal neurons.
(A) Confocal images of hippocampal neurons (15 DIV) infected with lentivirus containing EMPTY-EGFP, FAIM-L-EGFP, FAIM-L-shRNA or scrambled shRNA and immunolabeled against GFP (second column, green) and XIAP (third column, red). The scale bar represents 20 μm. (B) Quantification of XIAP staining relative to neuronal surface. A.U represent pixel intensities/μm2. N = 15 to 25 neurons from 3 independent experiments, for each group. Data represent mean ± SEM and One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison post-hoc test was used to calculate significant levels between the indicated groups. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. (C) Hippocampal neurons were infected with lentiviral vectors as indicated. Protein levels of XIAP and FAIM-L were determined by Western blot 48 h after infection with overexpressing and silencing vectors. Data are represented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of three independent experiments. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison post-hoc test was used to calculate significant levels between the indicated groups. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.