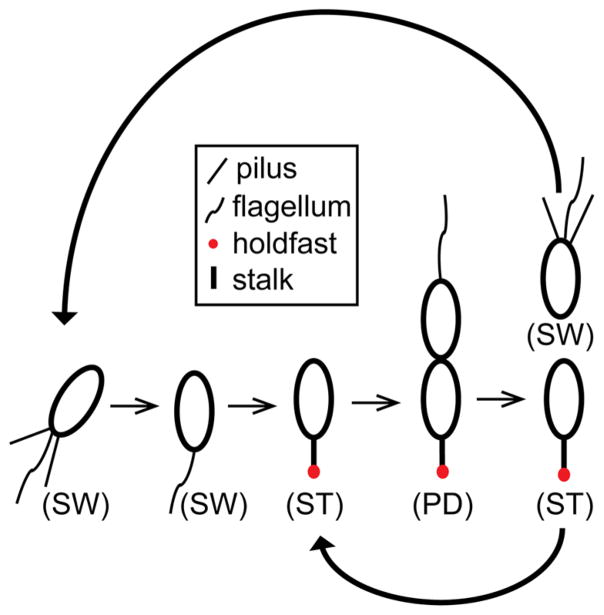
Figure 4.
Caulobacter crescentus cell cycle. Newborn motile swarmer cells (SW) have pili and a flagellum at the same pole and are unable to undergo DNA replication. After a motile period of 20–30 min, swarmer cells differentiate into sessile stalked cells (ST) by shedding their flagellum, retracting their pili, and synthesizing an adhesive holdfast and stalk from the same pole. Stalked cells initiate DNA replication, elongate, and synthesize a flagellum at the opposite pole of the stalk, forming a predivisional cell (PD). The predivisional cell subsequently divides into two daughter cells: one swarmer cell and one stalked cell. Repeated division of the stalked cell thus yields one new swarmer cell for each round of reproduction.